Effects of chromium picolinate on vascular reactivity and cardiac ischemia-reperfusion injury in spontaneously hypertensive rats
- PMID: 20885007
- PMCID: PMC3811011
- DOI: 10.1016/s1734-1140(10)70324-8
Effects of chromium picolinate on vascular reactivity and cardiac ischemia-reperfusion injury in spontaneously hypertensive rats
Abstract
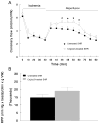
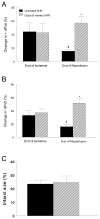
Chromium picolinate [Cr(pic)(3)] is a nutritional supplement widely promoted to exert beneficial metabolic effects in patients with type 2 diabetes/impaired glucose tolerance. Frequent comorbidities in these individuals include systemic hypertension, abnormal vascular function and ischemic heart disease, but information on the effects of the supplement on these aspects is sparse. Utilizing male spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR), we examined the potential impact of Cr(pic)(3) on blood pressure, vascular reactivity and myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury (IRI). Dietary Cr(pic)(3) supplementation (as 10 mg chromium/kg diet for six weeks) did not affect blood pressure of the SHR. Also, neither norepinephrine (NE) and potassium chloride (KCl)-induced contractility nor sodium nitroprusside (SNP)-induced relaxation of aortic smooth muscle from the SHR was altered by Cr(pic)(3) treatment. However, Cr(pic)(3) augmented endothelium-dependent relaxation of aortas, produced by acetylcholine (ACh), and this effect was abolished by N-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME), suggesting induction of nitric oxide (NO) production/release. Treatment with Cr(pic)(3) did not affect baseline coronary flow rate and rate-pressure-product (RPP) or infarct size following regional IRI. Nonetheless, Cr(pic)(3) treatment was associated with improved coronary flow and recovery of myocardial contractility and relaxation following ischemia-reperfusion insult. In conclusion, dietary Cr(pic)(3) treatment of SHR alters neither blood pressure nor vascular smooth muscle reactivity but causes enhancement of endothelium-dependent vasorelaxation associated with NO production/release. Additionally, while the treatment does not affect infarct size, it improves functional recovery of the viable portion of the myocardium following IRI.
Figures
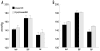
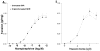
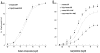
Similar articles
-
Endothelium-derived relaxing factor, hypertension and chronic parathyroidectomy in spontaneously hypertensive and Wistar-Kyoto rats.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 1993 Dec;20(12):773-85. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.1993.tb03015.x. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 1993. PMID: 8306520
-
Arterial contractions induced by cumulative addition of calcium in hypertensive and normotensive rats: influence of endothelium.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1994 Jun;349(6):627-36. doi: 10.1007/BF01258469. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1994. PMID: 7969514
-
Dietary calcium and magnesium supplements in spontaneously hypertensive rats and isolated arterial reactivity.Br J Pharmacol. 1995 Aug;115(8):1455-62. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1995.tb16637.x. Br J Pharmacol. 1995. PMID: 8564205 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancement of arterial relaxation by long-term atenolol treatment in spontaneously hypertensive rats.Br J Pharmacol. 1994 Jul;112(3):925-33. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb13169.x. Br J Pharmacol. 1994. PMID: 7921622 Free PMC article.
-
Hypertension and impairment of endothelium-dependent relaxation of arteries from spontaneously hypertensive and L-NAME-treated Wistar rats.J Smooth Muscle Res. 2001 Apr;37(2):67-79. doi: 10.1540/jsmr.37.67. J Smooth Muscle Res. 2001. PMID: 11592285
Cited by
-
Effects of chromium supplementation on physiology, feed intake, and insulin related metabolism in growing pigs subjected to heat stress.Transl Anim Sci. 2017 Feb;1(1):116-125. doi: 10.2527/tas2017.0014. Transl Anim Sci. 2017. PMID: 32704634 Free PMC article.
-
Supplementation of selenium, vitamin E, chromium and betaine above recommended levels improves lactating performance of sows over summer.Trop Anim Health Prod. 2017 Oct;49(7):1461-1469. doi: 10.1007/s11250-017-1348-y. Epub 2017 Jul 19. Trop Anim Health Prod. 2017. PMID: 28726110
-
Dietary Effects of Chromium Picolinate and Chromium Nanoparticles in Wistar Rats Fed with a High-Fat, Low-Fiber Diet: The Role of Fat Normalization.Nutrients. 2022 Dec 2;14(23):5138. doi: 10.3390/nu14235138. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36501167 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary nano chromium picolinate can ameliorate some of the impacts of heat stress in cross-bred sheep.Anim Nutr. 2021 Mar;7(1):198-205. doi: 10.1016/j.aninu.2020.07.004. Epub 2020 Dec 21. Anim Nutr. 2021. PMID: 33997348 Free PMC article.
-
The Impact of Chromium Supplementation on Blood Pressure: A Systematic Review and Dose-Response Meta‑Analysis of Randomized‑Controlled Trials.High Blood Press Cardiovasc Prev. 2021 Jul;28(4):333-342. doi: 10.1007/s40292-021-00456-8. Epub 2021 Jun 3. High Blood Press Cardiovasc Prev. 2021. PMID: 34081296
References
-
- Abebe W, Hussain T, Olanrewaju H, Mustafa SJ. Role of nitric oxide in adenosine receptor-mediated relaxation of porcine coronary artery. Am J Physiol. 1995;269:H1672–678. - PubMed
-
- Abebe W, Mozaffari MS. Effects of chronic taurine treatment on reactivity of the rat aorta. Amino Acids. 2000;19:615–623. - PubMed
-
- Abebe W, Mozaffari MS. Vascular reactivity changes in glucose-intolerant rat. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2007;50:590–597. - PubMed
-
- Abebe W. Effects of taurine on the reactivity of aortas from diabetic rats. Life Sci. 2008;82:279–289. - PubMed
-
- Anderson RA, Bryden NA, Polansky MM. Lack of toxicity of chromium chloride and chromium picolinate in rats. J Am Coll Nutr. 1997;16:273–279. - PubMed
