Hyperspectral Shack-Hartmann test
- PMID: 20885478
- PMCID: PMC3122479
- DOI: 10.1364/AO.49.005399
Hyperspectral Shack-Hartmann test
Abstract
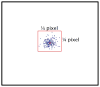
A hyperspectral Shack-Hartmann test bed has been developed to characterize the performance of miniature optics across a wide spectral range, a necessary first step in developing broadband achromatized all-polymer endomicroscopes. The Shack-Hartmann test bed was used to measure the chromatic focal shift (CFS) of a glass singlet lens and a glass achromatic lens, i.e., lenses representing the extrema of CFS magnitude in polymer elements to be found in endomicroscope systems. The lenses were tested from 500 to 700 nm in 5 and 10 nm steps, respectively. In both cases, we found close agreement between test results obtained from a ZEMAX model of the test bed and test lens and those obtained by experiment (maximum error of 12 μm for the singlet lens and 5 μm for the achromatic triplet lens). Future applications of the hyperspectral Shack-Hartmann test include measurements of aberrations as a function of wavelength, characterization of manufactured plastic endomicroscope elements and systems, and reverse optimization.
Figures


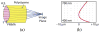




References
-
- Liang C. Miniature microscope objective lens. 7,023,622. US patent. 2006 April 4;
-
- McCall BP, Birch G, Descour MR, Tkaczyk TS. Fabrication of microlens array by diamond milling with spherical shaped milling tools. Proc SPIE. 2010;7590:75900A. (SPIE)
-
- Liang C, Descour MR, Sung KB, Richards-Kortum R. Fiber confocal reflectance microscope (FCRM) for in vivo imaging. Opt Express. 2001;9:821–830. - PubMed
-
- ISO Standard 19012–2. International Organization for Standardization; 2009. Photography—electronic still-picture cameras—resolution measurements.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

