Dementia revealed: novel chromosome 6 locus for late-onset Alzheimer disease provides genetic evidence for folate-pathway abnormalities
- PMID: 20885792
- PMCID: PMC2944795
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1001130
Dementia revealed: novel chromosome 6 locus for late-onset Alzheimer disease provides genetic evidence for folate-pathway abnormalities
Abstract
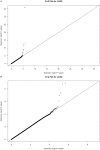
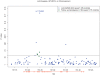
Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) of late-onset Alzheimer disease (LOAD) have consistently observed strong evidence of association with polymorphisms in APOE. However, until recently, variants at few other loci with statistically significant associations have replicated across studies. The present study combines data on 483,399 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) from a previously reported GWAS of 492 LOAD cases and 496 controls and from an independent set of 439 LOAD cases and 608 controls to strengthen power to identify novel genetic association signals. Associations exceeding the experiment-wide significance threshold (alpha=1.03x10(-7)) were replicated in an additional 1,338 cases and 2,003 controls. As expected, these analyses unequivocally confirmed APOE's risk effect (rs2075650, P=1.9x10(-36)). Additionally, the SNP rs11754661 at 151.2 Mb of chromosome 6q25.1 in the gene MTHFD1L (which encodes the methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase (NADP+ dependent) 1-like protein) was significantly associated with LOAD (P=4.70x10(-8); Bonferroni-corrected P=0.022). Subsequent genotyping of SNPs in high linkage disequilibrium (r2>0.8) with rs11754661 identified statistically significant associations in multiple SNPs (rs803424, P=0.016; rs2073067, P=0.03; rs2072064, P=0.035), reducing the likelihood of association due to genotyping error. In the replication case-control set, we observed an association of rs11754661 in the same direction as the previous association at P=0.002 (P=1.90x10(-10) in combined analysis of discovery and replication sets), with associations of similar statistical significance at several adjacent SNPs (rs17349743, P=0.005; rs803422, P=0.004). In summary, we observed and replicated a novel statistically significant association in MTHFD1L, a gene involved in the tetrahydrofolate synthesis pathway. This finding is noteworthy, as MTHFD1L may play a role in the generation of methionine from homocysteine and influence homocysteine-related pathways and as levels of homocysteine are a significant risk factor for LOAD development.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Replication of the MTHFD1L gene association with late-onset Alzheimer's disease in a Northern Han Chinese population.J Alzheimers Dis. 2012;29(3):521-5. doi: 10.3233/JAD-2011-111847. J Alzheimers Dis. 2012. PMID: 22330827
-
The MTHFD1L gene rs11754661 marker is not associated with Alzheimer's disease in a sample of the Spanish population.J Alzheimers Dis. 2011;25(1):47-50. doi: 10.3233/JAD-2011-101983. J Alzheimers Dis. 2011. PMID: 21383495
-
The MTHFD1L gene rs11754661 marker is associated with susceptibility to Alzheimer's disease in the Chinese Han population.J Neurol Sci. 2011 Sep 15;308(1-2):32-4. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2011.06.036. Epub 2011 Jul 8. J Neurol Sci. 2011. PMID: 21741665
-
Vitamin B-related Gene Polymorphisms and Cardiovascular Disease.Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2022;22(10):979-984. doi: 10.2174/1381612828666220328115605. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2022. PMID: 35346016 Review.
-
Genetic aspects of folate metabolism.Adv Hum Genet. 1979;9:293-354, 367-9. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-8276-2_5. Adv Hum Genet. 1979. PMID: 393094 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Alzheimer's genetics in the GWAS era: a continuing story of 'replications and refutations'.Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2011 Jun;11(3):246-53. doi: 10.1007/s11910-011-0193-z. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2011. PMID: 21487954 Review.
-
Hippocampal thinning linked to longer TOMM40 poly-T variant lengths in the absence of the APOE ε4 variant.Alzheimers Dement. 2017 Jul;13(7):739-748. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2016.12.009. Epub 2017 Feb 7. Alzheimers Dement. 2017. PMID: 28183529 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Influences on Plasma Homocysteine Levels in African Americans and Yoruba Nigerians.J Alzheimers Dis. 2016;49(4):991-1003. doi: 10.3233/JAD-150651. J Alzheimers Dis. 2016. PMID: 26519441 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome-wide piRNA profiling in human brains of Alzheimer's disease.Neurobiol Aging. 2017 Sep;57:170-177. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2017.05.020. Epub 2017 Jun 3. Neurobiol Aging. 2017. PMID: 28654860 Free PMC article.
-
Navigating the blurred boundary: Neuropathologic changes versus clinical symptoms in Alzheimer's disease, and its consequences for research in genetics.J Alzheimers Dis. 2025 Apr;104(3):611-626. doi: 10.1177/13872877251317543. Epub 2025 Feb 16. J Alzheimers Dis. 2025. PMID: 39956949 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alzheimer's Association. 2009 Alzheimer's Disease Facts and Figures. 2009. Washington, D.C. - PubMed
-
- Hebert LE, Scherr PA, Bienias JL, Bennett DA, Evans DA. Alzheimer disease in the US population: prevalence estimates using the 2000 census. Arch Neurol. 2003;60:1119–1122. - PubMed
-
- Goate A, Chartier-Harlin MC, Mullan M, Brown J, Crawford F, et al. Segregation of a missense mutation in the amyloid precursor protein gene with familial Alzheimer's disease. Nature. 1991;349:704–706. - PubMed
-
- Sherrington R, Rogaev EI, Liang Y, Rogaeva EA, Levesque G, et al. Cloning of a gene bearing missense mutations in early-onset familial Alzheimer's disease. Nature. 1995;375:754–760. - PubMed
-
- Levy-Lahad E, Lahad A, Wijsman EM, Bird TD, Schellenberg GD. Apolipoprotein E genotypes and age of onset in early-onset familial Alzheimer's disease. Ann Neurol. 1995;38:678–680. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- AG19757/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AG021886/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG010491/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG002219/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG027944/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG002219/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG027944/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- NS039764/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- AG005138/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS031153/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 NS039764/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS31153/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG010491/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG020135/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005138/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG019757/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AG21886/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG20135/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

