A Role of Staphyococcus aureus, Interleukin-18, Nerve Growth Factor and Semaphorin 3A, an Axon Guidance Molecule, in Pathogenesis and Treatment of Atopic Dermatitis
- PMID: 20885908
- PMCID: PMC2946701
- DOI: 10.4168/aair.2010.2.4.235
A Role of Staphyococcus aureus, Interleukin-18, Nerve Growth Factor and Semaphorin 3A, an Axon Guidance Molecule, in Pathogenesis and Treatment of Atopic Dermatitis
Abstract
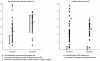
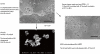
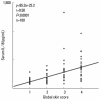
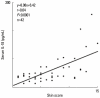
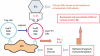
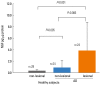
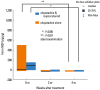
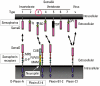
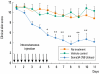
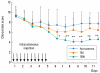
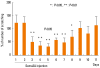
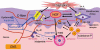
Staphylococcus aureus (SA) is usually present not only in the skin lesions of atopic dermatitis (AD) but also in the atopic dry skin. SA discharges various toxins and enzymes that injure the skin, results in activation of epidermal keratinocytes, which produce and release IL-18. IL-18 that induces the super Th1 cells secreting IFN-γ and IL-13 is supposed to be involved in development of AD and its pathogenesis. Indeed, the number of SA colonies on the skin surface and the serum IL-18 levels in patients with AD significantly correlated with the skin scores of AD lesions. Also, there is strong positive correlation between the skin scores and serum IL-18 levels in DS-Nh mice (P<0.0001, r=0.64), which develop considerable AD-like legions when they are housed under conventional conditions, but develop skin legions with less severity and less frequency under specific pathogens free (SPF) conditions. Therefore, they are well-known as model mice of AD, in which SA is presumed to be critical factor for the development of AD lesions. Also, theses DS-Nh mice pretreated with Cy developed more remarkable AD-like lesions in comparison with non-treated ones. The levels of INF-r and IL-13 in the supernatants of the lymph node cell cultures stimulated with staphylococcal enterotoxin B (SEB) or ConA were increased in the Cy-treated mice, although the serum levels of total IgE were not. In this experiment, we revealed that Cy-treated mice, to which CD25 +CD4 + reguratory T cells taken from non-treated ones had been transferred, developed the AD-like legions with less severity and less number of SA colonies on the skin surface. Therefore, it is presumed that CD25 +CD4 + reguratory T cells might be involved in the suppression of super Th1 cells which are induced by IL-18 and are involved in the development of AD-like lesions rather than IgE production. The efficient induction of CD25 +CD4 + reguratory T cells is expected for the new type of treatment of AD. We also found that farnesol (F) and xylitol (X) synergistically inhibited biofilm formation by SA, and indeed the ratio of SA in total bacteria at sites to which the FX cream containing F and X had been applied was significantly decreased 1 week later, accompanied with improvement of AD, when compared with that before application and at placebo sites. Therefore, the FX cream is a useful skin-care agent for atopic dry skin colonized by SA. The nerve growth factor (NGF) in the horny layer (the horn NGF) of skin lesions on the cubital fossa was collected by tape stripping and measured using ELISA in AD patients before and after 2 and 4 weeks treatments. Simultaneously, the itch and eruptions on the whole body and on the lesions, in which the horn NGF was measured, were recorded, and also the peripheral blood eosinophil count, serum LDH level and serum total IgE level were examined. The level of NGF was significantly higher in AD patients than in healthy controls, correlated with the severity of itch, erythema, scale/xerosis, the eosinophil count and LDH level, and also significantly decreased after treatments with olopatadine and/or steroid ointment for 2 and 4 weeks. Therefore, the measurement of the NGF by this harmless method seems to be useful to assess the severity of AD and the therapeutic effects on AD. In AD patients, C-fiber in the epidermis increase and sprout, inducing hypersensitivity, which is considered to aggravate the disease. Semaphorin 3A (Sema3A), an axon guidance molecule, is a potent inhibitor of neurite outgrowth of sensory neurons. We administered recombinant Sema3A intracutaneously into the skin lesions of NC/Nga mice, an animal model of AD, and investigated the effect of Sema3A on the skin lesions and their itch. Sema3A dose-dependently improved skin lesions and attenuated the scratching behavior in NC/Nga mice. Histological examinations revealed a decrease in the epidermal thickness, the density of invasive nerve fibers in the epidermis, inflammatory infiltrate including mast cells and CD4 +T cells, and the production of IL-4 in the Sema3A-treated lesions. Because the interruption of the itch-scratch cycle likely contributes to the improvement of the AD-like lesions, Sema3A is expected to become a promising treatment of patients with refractory AD.
Keywords: Atopic dermatitis; Semaphorin 3A; Staphylococcus aureus; nerve growth factor.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no financial or other issues that might lead to conflict of interest.
Figures



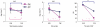
Similar articles
-
Semaphorin3A alleviates skin lesions and scratching behavior in NC/Nga mice, an atopic dermatitis model.J Invest Dermatol. 2008 Dec;128(12):2842-9. doi: 10.1038/jid.2008.150. Epub 2008 Jul 10. J Invest Dermatol. 2008. PMID: 18615113
-
Quantitative analysis of nerve growth factor (NGF) in the atopic dermatitis and psoriasis horny layer and effect of treatment on NGF in atopic dermatitis.J Dermatol Sci. 2009 Jan;53(1):48-54. doi: 10.1016/j.jdermsci.2008.08.011. Epub 2008 Oct 14. J Dermatol Sci. 2009. PMID: 18922683
-
Substance P restores normal skin architecture and reduces epidermal infiltration of sensory nerve fiber in TNCB-induced atopic dermatitis-like lesions in NC/Nga mice.J Dermatol Sci. 2018 Mar;89(3):248-257. doi: 10.1016/j.jdermsci.2017.11.013. Epub 2017 Dec 1. J Dermatol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29269174
-
Mechanisms of Itch in Atopic Dermatitis.Juntendo Med J. 2025 Jan 30;71(1):43-50. doi: 10.14789/ejmj.JMJ24-0036-R. eCollection 2025. Juntendo Med J. 2025. PMID: 40109398 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Itch and nerve fibers with special reference to atopic dermatitis: therapeutic implications.J Dermatol. 2014 Mar;41(3):205-12. doi: 10.1111/1346-8138.12317. J Dermatol. 2014. PMID: 24628070 Review.
Cited by
-
Inflammatory cytokines and biofilm production sustain Staphylococcus aureus outgrowth and persistence: a pivotal interplay in the pathogenesis of Atopic Dermatitis.Sci Rep. 2018 Jun 28;8(1):9573. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-27421-1. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29955077 Free PMC article.
-
Skin neuropathy and immunomodulation in diseases.Fundam Res. 2022 Sep 8;4(2):218-225. doi: 10.1016/j.fmre.2022.08.016. eCollection 2024 Mar. Fundam Res. 2022. PMID: 38933512 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neurogenic markers of the inflammatory process in atopic dermatitis: relation to the severity and pruritus.Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 2013 Oct;30(5):286-92. doi: 10.5114/pdia.2013.38357. Epub 2013 Oct 30. Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 2013. PMID: 24353488 Free PMC article.
-
CSP0510 Lotion as a Novel Moisturizer Containing Citric Acid and Trisodium Phosphate Relieves Objective and Subjective Symptoms of Atopic Dermatitis.Ann Dermatol. 2016 Jun;28(3):344-51. doi: 10.5021/ad.2016.28.3.344. Epub 2016 May 25. Ann Dermatol. 2016. PMID: 27274633 Free PMC article.
-
Semaphorin 3A: A potential target for prevention and treatment of nickel allergy.Commun Biol. 2022 Jul 7;5(1):671. doi: 10.1038/s42003-022-03641-0. Commun Biol. 2022. PMID: 35798870 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kanbara T, Nakamura K, Tanaka Y, Inoue Y, Tanaka K, Ikezawa Z. A study about the prevalence of infantile atopic dermatitis (the 5th report) Proceedings in Arerugi. 2009;58:376.
-
- Katsuyama M, Wachi Y, Kitamura K, Suga C, Onuma S, Ikezawa Z. Correlation between the population of staphylococcus aureus on the skin and severity of score of dry type atopic dermatitis condition. Nippon Hifuka Gakkai Zasshi. 1997;107:1103–1111.
-
- Katsuyama M, Ichikawa H, Ogawa S, Ikezawa Z. A novel method to control the balance of skin microflora. Part 1. Attack on biofilm of Staphylococcus aureus without antibiotics. J Dermatol Sci. 2005;38:197–205. - PubMed
-
- Katsuyama M, Kobayashi Y, Ichikawa H, Mizuno A, Miyachi Y, Matsunaga K, Kawashima M. A novel method to control the balance of skin microflora Part 2. A study to assess the effect of a cream containing farnesol and xylitol on atopic dry skin. J Dermatol Sci. 2005;38:207–213. - PubMed
-
- Fujita H, Takahashi H, Aihara M, Hirasawa T, Ikezawa Z. Effects of bamboo leaf extract on atopic dermatitis model mice. J Environ Dermatol. 2006;13:87–94.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

