Implementation of compressed sensing in telecardiology sensor networks
- PMID: 20885973
- PMCID: PMC2946575
- DOI: 10.1155/2010/127639
Implementation of compressed sensing in telecardiology sensor networks
Abstract
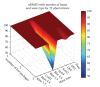
Mobile solutions for patient cardiac monitoring are viewed with growing interest, and improvements on current implementations are frequently reported, with wireless, and in particular, wearable devices promising to achieve ubiquity. However, due to unavoidable power consumption limitations, the amount of data acquired, processed, and transmitted needs to be diminished, which is counterproductive, regarding the quality of the information produced. Compressed sensing implementation in wireless sensor networks (WSNs) promises to bring gains not only in power savings to the devices, but also with minor impact in signal quality. Several cardiac signals have a sparse representation in some wavelet transformations. The compressed sensing paradigm states that signals can be recovered from a few projections into another basis, incoherent with the first. This paper evaluates the compressed sensing paradigm impact in a cardiac monitoring WSN, discussing the implications in data reliability, energy management, and the improvements accomplished by in-network processing.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Sparse Recovery Optimization in Wireless Sensor Networks with a Sub-Nyquist Sampling Rate.Sensors (Basel). 2015 Jul 10;15(7):16654-73. doi: 10.3390/s150716654. Sensors (Basel). 2015. PMID: 26184203 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Wireless Transmission Method for Large Data Based on Hierarchical Compressed Sensing and Sparse Decomposition.Sensors (Basel). 2020 Dec 13;20(24):7146. doi: 10.3390/s20247146. Sensors (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33322189 Free PMC article.
-
A Non-Convex Compressed Sensing Model Improving the Energy Efficiency of WSNs for Abnormal Events' Monitoring.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Nov 1;22(21):8378. doi: 10.3390/s22218378. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36366078 Free PMC article.
-
Exploiting prior knowledge in compressed sensing wireless ECG systems.IEEE J Biomed Health Inform. 2015 Mar;19(2):508-19. doi: 10.1109/JBHI.2014.2325017. Epub 2014 May 16. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform. 2015. PMID: 24846672
-
A Review of Advanced Localization Techniques for Crowdsensing Wireless Sensor Networks.Sensors (Basel). 2019 Feb 26;19(5):988. doi: 10.3390/s19050988. Sensors (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30813541 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A low-complexity photoplethysmographic systolic peak detector for compressed sensed data.Physiol Meas. 2019 Jul 1;40(6):065007. doi: 10.1088/1361-6579/ab254b. Physiol Meas. 2019. PMID: 31141798 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Römer K, Mattern F. The design space of wireless sensor networks. IEEE Wireless Communications. 2004;11(6):54–61.
-
- Finapres Medical Systems. http://www.finapres.com/
-
- Muehlsteff J, Aubert XA, Morren G. Continuous cuff-less blood pressure monitoring based on the pulse arrival time approach: the impact of posture. In: Proceedings of the 30th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBS ’08); August 2008; Vancouver, Canada. pp. 1691–1694. - PubMed
-
- Pinheiro E, Postolache O. A wireless monitoring system for health care applications. In: Proceedings of the 6th IASTED International Conference on Biomedical Engineering (BioMED ’08); February 2008; Innsbruck, Austria. pp. 372–377.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

