Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A3 is the liver nuclear protein binding to age related increase element RNA of the factor IX gene
- PMID: 20885981
- PMCID: PMC2945768
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012971
Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A3 is the liver nuclear protein binding to age related increase element RNA of the factor IX gene
Abstract
Background: In the ASE/AIE-mediated genetic mechanism for age-related gene regulation, a recently identified age-related homeostasis mechanism, two genetic elements, ASE (age-related stability element) and AIE (age-related increase element as a stem-loop forming RNA), play critical roles in producing specific age-related expression patterns of genes.
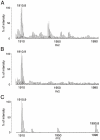
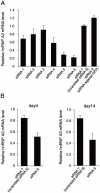
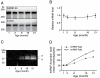
Principal finding: We successfully identified heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A3 (hnRNP A3) as a major mouse liver nuclear protein binding to the AIE-derived RNAs of human factor IX (hFIX) as well as mouse factor IX (mFIX) genes. HnRNP A3 bound to the AIE RNA was not phosphorylated at its Ser(359), while hnRNP A3 in the mouse liver nuclear extracts was a mixture of phosphorylated and unphosphorylated Ser(359). HepG2 cells engineered to express recombinant hFIX transduced with adenoviral vectors harboring an effective siRNA against hnRNP A3 resulted in a substantial reduction in hFIX expression only in the cells carrying a hFIX expression vector with AIE, but not in the cells carrying a hFIX expression vector without AIE. The nuclear hnRNP A3 protein level in the mouse liver gradually increased with age, while its mRNA level stayed age-stable.
Conclusions: We identified hnRNP A3 as a major liver nuclear protein binding to FIX-AIE RNA. This protein plays a critical role in age-related gene expression, likely through an as yet unidentified epigenetic mechanism. The present study assigned a novel functional role to hnRNP A3 in age-related regulation of gene expression, opening up a new avenue for studying age-related homeostasis and underlying molecular mechanisms.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
hnRNP A1 mediates the activation of the IRES-dependent SREBP-1a mRNA translation in response to endoplasmic reticulum stress.Biochem J. 2013 Jan 15;449(2):543-53. doi: 10.1042/BJ20120906. Biochem J. 2013. PMID: 23106379
-
Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A3, a novel RNA trafficking response element-binding protein.J Biol Chem. 2002 May 17;277(20):18010-20. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M200050200. Epub 2002 Mar 8. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 11886857
-
Synergistic stimulation of HIV-1 rev-dependent export of unspliced mRNA to the cytoplasm by hnRNP A1.J Mol Biol. 1999 Feb 5;285(5):1951-64. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1998.2473. J Mol Biol. 1999. PMID: 9925777
-
Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A1 in health and neurodegenerative disease: from structural insights to post-transcriptional regulatory roles.Mol Cell Neurosci. 2013 Sep;56:436-46. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2012.12.002. Epub 2012 Dec 14. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23247072 Review.
-
Emerging roles of hnRNP A2B1 in cancer and inflammation.Int J Biol Macromol. 2022 Nov 30;221:1077-1092. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.09.104. Epub 2022 Sep 13. Int J Biol Macromol. 2022. PMID: 36113587 Review.
Cited by
-
Immunity Depletion, Telomere Imbalance, and Cancer-Associated Metabolism Pathway Aberrations in Intestinal Mucosa upon Short-Term Caloric Restriction.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Jun 25;13(13):3180. doi: 10.3390/cancers13133180. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34202278 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative Stress and Thrombosis during Aging: The Roles of Oxidative Stress in RBCs in Venous Thrombosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jun 15;21(12):4259. doi: 10.3390/ijms21124259. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32549393 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Age-related expression analysis of mouse liver nuclear protein binding to 3'-untranslated region of Period2 gene.J Physiol Sci. 2015 Jul;65(4):349-57. doi: 10.1007/s12576-015-0373-8. Epub 2015 Apr 7. J Physiol Sci. 2015. PMID: 25846207 Free PMC article.
-
DNA methylome and transcriptome sequencing in human ovarian granulosa cells links age-related changes in gene expression to gene body methylation and 3'-end GC density.Oncotarget. 2015 Feb 28;6(6):3627-43. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.2875. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 25682867 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kurachi S, Deyashiki Y, Takeshita J, Kurachi K. Genetic mechanisms of age regulation of human blood coagulation factor IX. Science. 1999;285:739–743. - PubMed
-
- Zhang K, Kurachi S, Kurachi K. Genetic mechanisms of age regulation of protein C and blood coagulation. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:4532–4540. - PubMed
-
- Kurachi K, Kurachi S. Molecular mechanisms of age-related regulation of genes. J Thromb Haemost. 2005;3:909–914. - PubMed
-
- Yoshitake S, Schach BG, Foster DC, Davie EW, Kurachi K. Nucleotide sequence of the gene for human factor IX (antihemophilic factor B). Biochemistry. 1985;24:3736–3750. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

