The Plk1 inhibitor BI 2536 temporarily arrests primary cardiac fibroblasts in mitosis and generates aneuploidy in vitro
- PMID: 20886032
- PMCID: PMC2945759
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012963
The Plk1 inhibitor BI 2536 temporarily arrests primary cardiac fibroblasts in mitosis and generates aneuploidy in vitro
Abstract
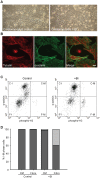
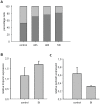
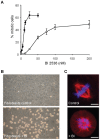
BI 2536 is a new anti-mitotic drug that targets polo-like kinase 1 (Plk1) and is currently under clinical development for cancer therapy. The effect of this drug on cancer cells has been extensively investigated, but information about the effects on primary dividing cells and differentiated non-dividing cells is scarce. We have investigated the effects of this drug on primary neonatal rat cardiac fibroblasts and on differentiated cardiomyocytes and explored the possibility to use this drug to enrich differentiated cell populations in vitro. BI 2536 had a profound effect on cardiac fibroblast proliferation in vitro and arrested these cells in mitosis with an IC50 of about 43 nM. Similar results were observed with primary human cells (HUVEC, IC50 = 30 nM), whereas the cancer cell line HeLa was more sensitive (IC50 of 9 nM). Further analysis revealed that prolonged mitotic arrest resulted in cell death for about 40% of cardiac fibroblasts. The remaining cells showed an interphase morphology with mostly multi- and micro-nucleated nuclei. This indicates that a significant number of primary fibroblasts are able to escape BI 2536 induced mitotic arrest and apparently become aneuploid. No effects were observed on cardiomyocytes and hypertrophic response (growth) upon endothelin-1 and phenylephrine stimulation was normal in the presence of BI 2536. This indicates that BI 2536 has no adverse effects on terminally differentiated cells and still allows proliferation independent growth induction in these cells. In conclusion, cardiomyocytes could be enriched using BI 2536, but the formation of aneuploidy in proliferating cells most likely limits this in vitro application and does not allow its use in putative cell based therapies.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
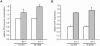
Similar articles
-
Co-inhibition of polo-like kinase 1 and Aurora kinases promotes mitotic catastrophe.Oncotarget. 2015 Apr 20;6(11):9327-40. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3313. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 25871386 Free PMC article.
-
Differential Cellular Effects of Plk1 Inhibitors Targeting the ATP-binding Domain or Polo-box Domain.J Cell Physiol. 2015 Dec;230(12):3057-67. doi: 10.1002/jcp.25042. J Cell Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25975351
-
Impact of Polo-like kinase 1 inhibitors on human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells.Oncotarget. 2016 Dec 20;7(51):84271-84285. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12482. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27713178 Free PMC article.
-
BI_2536--targeting the mitotic kinase Polo-like kinase 1 (Plk1).Recent Results Cancer Res. 2010;184:215-8. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-01222-8_15. Recent Results Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20072841 Review.
-
Non-mitotic functions of polo-like kinases in cancer cells.Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2021 Jan;1875(1):188467. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2020.188467. Epub 2020 Nov 7. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33171265 Review.
Cited by
-
In vitro effects of pirfenidone on cardiac fibroblasts: proliferation, myofibroblast differentiation, migration and cytokine secretion.PLoS One. 2011;6(11):e28134. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0028134. Epub 2011 Nov 23. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 22132230 Free PMC article.
-
An antibody fragment functionalized dendritic PEGylated poly(2-(dimethylamino)ethyl diacrylate) as a vehicle of exogenous microRNA.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2012 Oct;2(5):406-14. doi: 10.1007/s13346-012-0097-8. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2012. PMID: 25787178
-
Boolean model of growth signaling, cell cycle and apoptosis predicts the molecular mechanism of aberrant cell cycle progression driven by hyperactive PI3K.PLoS Comput Biol. 2019 Mar 15;15(3):e1006402. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1006402. eCollection 2019 Mar. PLoS Comput Biol. 2019. PMID: 30875364 Free PMC article.
-
Polo-like kinase 1 inhibitors, mitotic stress and the tumor suppressor p53.Cell Cycle. 2013 May 1;12(9):1340-51. doi: 10.4161/cc.24573. Epub 2013 Apr 10. Cell Cycle. 2013. PMID: 23574746 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing Gene-Knockdown Efficiency of Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) Nanogels.ACS Omega. 2018 Jul 31;3(7):8042-8049. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.8b00738. Epub 2018 Jul 18. ACS Omega. 2018. PMID: 30087933 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Maass AH, Buvoli M. Cardiomyocyte preparation, culture, and gene transfer. Methods Mol Biol. 2007;366:321–330. - PubMed
-
- Ren D, Miller JD. Primary cell culture of suprachiasmatic nucleus. Brain Res Bull. 2003;61:547–553. - PubMed
-
- Lenart P, Petronczki M, Steegmaier M, Di Fiore B, Lipp JJ, et al. The small-molecule inhibitor BI 2536 reveals novel insights into mitotic roles of polo-like kinase 1. Curr Bio. 2007;17:304–315. - PubMed
-
- Steegmaier M, Hoffmann M, Baum A, Lenart P, Petronczki M, et al. BI 2536, a potent and selective inhibitor of polo-like kinase 1, inhibits tumor growth in vivo. Curr Biol. 2007;17:316–322. - PubMed
-
- Barr FA, Sillje HH, Nigg EA. Polo-like kinases and the orchestration of cell division. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2004;5:429–440. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

