Suppression of uPAR retards radiation-induced invasion and migration mediated by integrin β1/FAK signaling in medulloblastoma
- PMID: 20886051
- PMCID: PMC2945321
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0013006
Suppression of uPAR retards radiation-induced invasion and migration mediated by integrin β1/FAK signaling in medulloblastoma
Retraction in
-
Retraction: Suppression of uPAR retards radiation-induced invasion and migration mediated by integrin β1/FAK signaling in medulloblastoma.PLoS One. 2025 Jul 15;20(7):e0328091. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0328091. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40663494 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
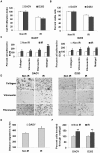
Background: Despite effective radiotherapy for the initial stages of cancer, several studies have reported the recurrence of various cancers, including medulloblastoma. Here, we attempt to capitalize on the radiation-induced aggressive behavior of medulloblastoma cells by comparing the extracellular protease activity and the expression pattern of molecules, known to be involved in cell adhesion, migration and invasion, between non-irradiated and irradiated cells.
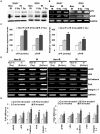
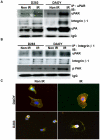
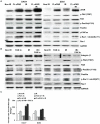
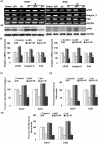
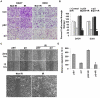
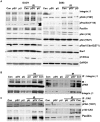
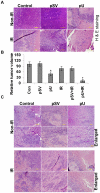
Methodology/principal findings: We identified an increase in invasion and migration of irradiated compared to non-irradiated medulloblastoma cells. RT-PCR analysis confirmed increased expression of uPA, uPAR, focal adhesion kinase (FAK), N-Cadherin and integrin subunits (e.g., α3, α5 and β1) in irradiated cells. Furthermore, we noticed a ∼2-fold increase in tyrosine phosphorylation of FAK in irradiated cells. Immunoprecipitation studies confirmed increased interaction of integrin β1 and FAK in irradiated cells. In addition, our results show that overexpression of uPAR in cancer cells can mimic radiation-induced activation of FAK signaling. Moreover, by inhibiting FAK phosphorylation, we were able to reduce the radiation-induced invasiveness of the cancer cells. In this vein, we studied the effect of siRNA-mediated knockdown of uPAR on cell migration and adhesion in irradiated and non-irradiated medulloblastoma cells. Downregulation of uPAR reduced the radiation-induced adhesion, migration and invasion of the irradiated cells, primarily by inhibiting phosphorylation of FAK, Paxillin and Rac-1/Cdc42. As observed from the immunoprecipitation studies, uPAR knockdown reduced interaction among the focal adhesion molecules, such as FAK, Paxillin and p130Cas, which are known to play key roles in cancer metastasis. Pretreatment with uPAR shRNA expressing construct reduced uPAR and phospho FAK expression levels in pre-established medulloblastoma in nude mice.
Conclusion/significance: Taken together, our results show that radiation enhances uPAR-mediated FAK signaling and by targeting uPAR we can inhibit radiation-activated cell adhesion and migration both in vitro and in vivo.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Apoptosis induced by knockdown of uPAR and MMP-9 is mediated by inactivation of EGFR/STAT3 signaling in medulloblastoma.PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e44798. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0044798. Epub 2012 Sep 12. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22984561 Free PMC article.
-
MMP-9, uPAR and cathepsin B silencing downregulate integrins in human glioma xenograft cells in vitro and in vivo in nude mice.PLoS One. 2010 Jul 15;5(7):e11583. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0011583. PLoS One. 2010. Retraction in: PLoS One. 2025 Jul 11;20(7):e0328092. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0328092. PMID: 20657647 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Suppression of uPA and uPAR attenuates angiogenin mediated angiogenesis in endothelial and glioblastoma cell lines.PLoS One. 2010 Aug 27;5(8):e12458. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012458. PLoS One. 2010. Retraction in: PLoS One. 2025 Aug 14;20(8):e0330088. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0330088. PMID: 20805979 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Chemotherapy for children with medulloblastoma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Jan 1;1(1):CD006678. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006678.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 25879092 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
Cited by
-
Radiation-induced motility alterations in medulloblastoma cells.J Radiat Res. 2015 May;56(3):430-6. doi: 10.1093/jrr/rru120. Epub 2015 Mar 2. J Radiat Res. 2015. PMID: 25736470 Free PMC article.
-
SPRY1 promotes the degradation of uPAR and inhibits uPAR-mediated cell adhesion and proliferation.Am J Cancer Res. 2014 Nov 19;4(6):683-97. eCollection 2014. Am J Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 25520860 Free PMC article.
-
Arf6-driven cell invasion is intrinsically linked to TRAK1-mediated mitochondrial anterograde trafficking to avoid oxidative catastrophe.Nat Commun. 2018 Jul 11;9(1):2682. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-05087-7. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 29992963 Free PMC article.
-
Knockdown of cathepsin B and uPAR inhibits CD151 and α3β1 integrin-mediated cell adhesion and invasion in glioma.Mol Carcinog. 2013 Oct;52(10):777-90. doi: 10.1002/mc.21915. Epub 2012 Apr 11. Mol Carcinog. 2013. Retraction in: Mol Carcinog. 2021 Oct;60(10):717. doi: 10.1002/mc.23342. PMID: 22495828 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Crosstalk between EGFR and integrin affects invasion and proliferation of gastric cancer cell line, SGC7901.Onco Targets Ther. 2012;5:271-7. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S35322. Epub 2012 Oct 23. Onco Targets Ther. 2012. Retraction in: Onco Targets Ther. 2025 Jun 10;18:733-734. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S544936. PMID: 23109808 Free PMC article. Retracted.
References
-
- Crawford JR, MacDonald TJ, Packer RJ. Medulloblastoma in childhood: new biological advances. Lancet Neurol. 2007;6:1073–1085. - PubMed
-
- Howes TL, Buatti JM, Kirby PA, Carlisle TL, Ryken TC. Radiation induced adult medulloblastoma: a case report. J Neurooncol. 2006;80:191–194. - PubMed
-
- Chan MY, Teo WY, Seow WT, Tan AM. Epidemiology, management and treatment outcome of medulloblastoma in singapore. Ann Acad Med Singapore. 2007;36:314–318. - PubMed
-
- Feltbower RG, Picton S, Bridges LR, Crooks DA, Glaser AW, et al. Epidemiology of central nervous system tumors in children and young adults (0–29 years), Yorkshire, United Kingdom. Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2004;21:647–660. - PubMed
-
- Ranger A, McDonald W, Bauman GS, Del MR. Effects of surgical excision and radiation on medulloblastoma cell invasiveness. Can J Neurol Sci. 2009;36:631–637. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

