An exocyclic methylene group acts as a bioisostere of the 2'-oxygen atom in LNA
- PMID: 20886816
- PMCID: PMC2993159
- DOI: 10.1021/ja105875e
An exocyclic methylene group acts as a bioisostere of the 2'-oxygen atom in LNA
Abstract
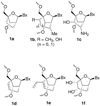
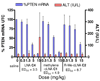
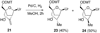
We show for the first time that it is possible to obtain LNA-like (Locked Nucleic Acid 1) binding affinity and biological activity with carbocyclic LNA (cLNA) analogs by replacing the 2'-oxygen atom in LNA with an exocyclic methylene group. Synthesis of the methylene-cLNA nucleoside was accomplished by an intramolecular cyclization reaction between a radical at the 2'-position and a propynyl group at the C-4' position. Only methylene-cLNA modified oligonucleotides showed similar thermal stability and mismatch discrimination properties for complementary nucleic acids as LNA. In contrast, the close structurally related methyl-cLNA analogs showed diminished hybridization properties. Analysis of crystal structures of cLNA modified self-complementary DNA decamer duplexes revealed that the methylene group participates in a tight interaction with a 2'-deoxyribose residue of the 5'-terminal G of a neighboring duplex, resulting in the formation of a CH...O type hydrogen bond. This indicates that the methylene group retains a negative polarization at the edge of the minor groove in the absence of a hydrophilic 2'-substituent and provides a rationale for the superior thermal stability of this modification. In animal experiments, methylene-cLNA antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs) showed similar in vivo activity but reduced toxicity as compared to LNA ASOs. Our work highlights the interchangeable role of oxygen and unsaturated moieties in nucleic acid structure and emphasizes greater use of this bioisostere to improve the properties of nucleic acids for therapeutic and diagnostic applications.
Figures




References
-
- Bennett CF, Swayze EE. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2010;50:259–293. - PubMed
-
- Swayze EE, Bhat BIn. In: Antisense Drug Technology: Principles, Strategies, and Applications. 2nd ed. Crooke ST, editor. Boca Raton: CRC Press; 2008. pp. 143–182.
-
- Eckstein F. Antisense Nucleic Acid Drug Dev. 2000;10:117–121. - PubMed
-
- Geary RS, Yu RZ, Levin AA. Curr. Opin. Investig. Drugs. 2001;2:562–573. - PubMed
-
- Martin P. Helv. Chim. Acta. 1995;78:486–504.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

