Combination of photodynamic therapy with aspirin in human-derived lung adenocarcinoma cells affects proteasome activity and induces apoptosis
- PMID: 20887554
- PMCID: PMC6495995
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2184.2010.00698.x
Combination of photodynamic therapy with aspirin in human-derived lung adenocarcinoma cells affects proteasome activity and induces apoptosis
Abstract
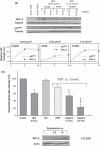
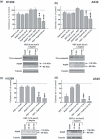
Objectives: Photodynamic treatment (PDT) of human lung carcinoma cells A549 (p53(+/+)) and H1299 (p53(-/-)) induces fast but transient stalling of proteasome activity. We have explored the possibility of prolonging this effect by combining PDT with drugs capable of sustaining the stall, and promote apoptosis of surviving cells. We show that aspirin can be used to accomplish this.
Materials and methods: Cells were irradiated at doses ranging from 0.54 to 1.10 J cm(-2), and subsequently were incubated with aspirin at either high (10 and 5 mm) or low concentration (2.5 and 1.5 mm). Photofrin concentration and incubation time were constant (2.5 μg/ml and 16 h). Under these conditions, we analysed cell viability, colony-forming efficiency, cycle profile, expression patterns of specific proteins and ubiquitination state, after individual or combined administration.
Results: Treatment with either PDT or aspirin, rapidly induced proteasome malfunction and accumulation of cells in G(2)M, but did not induce apoptosis. However, when aspirin was added to cells (even at low concentrations) after PDT, the proteasome block was sustained. Moreover, significant cytotoxic effects, including apoptosis, were observed along with cytostatic effects (G(2)M accumulation/decreased colony formation).
Conclusions: Combination of PDT and low-toxicity drugs (such as aspirin) resulted in protracted inhibition of proteasome activity and induced apoptosis even in apoptosis-resistant cancer cells.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Photodynamic therapy with 5-aminolaevulinic acid and DNA damage: unravelling roles of p53 and ABCG2.Cell Prolif. 2016 Aug;49(4):523-38. doi: 10.1111/cpr.12274. Epub 2016 Jul 7. Cell Prolif. 2016. PMID: 27389299 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial Malfunctioning, Proteasome Arrest and Apoptosis in Cancer Cells by Focused Intracellular Generation of Oxygen Radicals.Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Aug 28;16(9):20375-91. doi: 10.3390/ijms160920375. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26343643 Free PMC article.
-
Light dose effect of photodynamic therapy on growth inhibition and apoptosis induction in non-small cell lung cancer: A study in nude mouse model.Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. 2023 Dec;44:103865. doi: 10.1016/j.pdpdt.2023.103865. Epub 2023 Nov 9. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. 2023. PMID: 37949389
-
Proteasome inhibitors in lung cancer.Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2006 Jun;58(3):177-89. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2005.12.001. Epub 2006 Jan 19. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2006. PMID: 16427303 Review.
-
Clinical Practice of Photodynamic Therapy for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer in Different Scenarios: Who Is the Better Candidate?Respiration. 2024;103(4):193-204. doi: 10.1159/000535270. Epub 2024 Feb 16. Respiration. 2024. PMID: 38354707 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
5-aminolaevulinic acid/photo-dynamic therapy and gefitinib in non-small cell lung cancer cell lines: a potential strategy to improve gefitinib therapeutic efficacy.Cell Prolif. 2013 Aug;46(4):382-95. doi: 10.1111/cpr.12040. Cell Prolif. 2013. PMID: 23869760 Free PMC article.
-
New hydrophilic/lipophilic tetra-α-(4-carboxyphenoxy) phthalocyanine zinc-mediated photodynamic therapy inhibits the proliferation of human hepatocellular carcinoma Bel-7402 cells by triggering apoptosis and arresting cell cycle.Molecules. 2011 Feb 7;16(2):1389-401. doi: 10.3390/molecules16021389. Molecules. 2011. PMID: 21301411 Free PMC article.
-
Photodynamic therapy with 5-aminolaevulinic acid and DNA damage: unravelling roles of p53 and ABCG2.Cell Prolif. 2016 Aug;49(4):523-38. doi: 10.1111/cpr.12274. Epub 2016 Jul 7. Cell Prolif. 2016. PMID: 27389299 Free PMC article.
-
Targets and mechanisms of photodynamic therapy in lung cancer cells: a brief overview.Cancers (Basel). 2011 Mar 3;3(1):1014-41. doi: 10.3390/cancers3011014. Cancers (Basel). 2011. PMID: 24212652 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing photodynamyc therapy efficacy by combination therapy: dated, current and oncoming strategies.Cancers (Basel). 2011 Jun 9;3(2):2597-629. doi: 10.3390/cancers3022597. Cancers (Basel). 2011. PMID: 24212824 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Orlowski RZ (1999) The role of the ubiquitin‐proteasome pathway in apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 6, 303–313. - PubMed
-
- Adams J (2004) The proteasome: a suitable antineoplastic target. Nat. Rev. Cancer 4, 349–360. - PubMed
-
- Karin M, Yamamoto Y, Wang QM (2004) The IKK NF‐kappaB system: a treasure trove for drug development. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 3, 17–26. - PubMed
-
- Hershko A (1997) Roles of ubiquitin‐mediated proteolysis in cell cycle control. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 9, 788–799. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

