The 6-minute walk is associated with frailty and predicts mortality in older adults with heart failure
- PMID: 20887617
- PMCID: PMC3027222
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1751-7133.2010.00151.x
The 6-minute walk is associated with frailty and predicts mortality in older adults with heart failure
Abstract
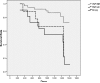
Heart failure (HF) may contribute to the development of functional decline and frailty in older adults. Sixty HF patients with an ejection fraction ≤ 40% evaluated in 2004 and 2005 were reevaluated in 2008. Six-minute walk distance (6MW), frailty score, and biomarkers (25-hydroxyvitamin D, C-reactive protein, and interleukin-6 [IL-6]) were measured. Participants were categorized at baseline and follow-up into 3 groups: nonfrail/normal endurance (NF/NE), nonfrail/low endurance (NF/LE) and frail/low endurance (F/LE). Survival time was assessed according to frailty/endurance status and associated predictors of mortality. Forty-three men, 17 women (mean age, 78 ± 12 years) were contacted. At follow-up, 20 had died, 20 participated, and 20 did not participate. There were no changes in frailty/endurance status over time (McNemar;P=.19). Deaths occurred in 18% of NF/NE, 45% of NF/LE, and 60% of F/LE persons. The NF/NE group had greater survival rates than the NF/LE ( P=.032) and F/LE ( P=.014) groups. The 6MW and frailty score were independently predictive of mortality, with hazard ratios of 0.82 (95% confidence interval, 0.72-0.94) and 1.64 (95% confidence interval, 1.19-2.26), respectively, as was New York Heart Association class and IL-6. Backward stepwise Cox regression revealed that 6MW and frailty each were associated with mortality (P=.005) and highly correlated. Physical function is an important predictor of mortality in older adults with HF. The 6MW may be useful as a measure of frailty.
© 2010 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Lloyd-Jones D, Adams R, Carnethon M, De Simone G, Ferguson TB, Flegal K, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics--2009 update: a report from the American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Circulation. 2009;119(3):480–6. - PubMed
-
- Jencks SF, Williams MV, Coleman EA. Rehospitalizations among patients in the Medicare fee-for-service program. N Engl J Med. 2009;360(14):1418–28. - PubMed
-
- Fang J, Mensah GA, Croft JB, Keenan NL. Heart failure-related hospitalization in the U.S., 1979 to 2004. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2008;52(6):428–34. - PubMed
-
- Boyd CM, Xue QL, Guralnik JM, Fried LP. Hospitalization and development of dependence in activities of daily living in a cohort of disabled older women: the Women's Health and Aging Study I. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2005;60(7):888–93. - PubMed
-
- Fried LP, Tangen CM, Walston J, Newman AB, Hirsch C, Gottdiener J, et al. Frailty in older adults: evidence for a phenotype. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2001;56(3):M146–56. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous