β₂ AR agonists in treatment of chronic heart failure: long path to translation
- PMID: 20888833
- PMCID: PMC3051013
- DOI: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2010.09.019
β₂ AR agonists in treatment of chronic heart failure: long path to translation
Abstract
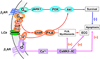
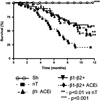
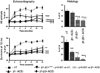
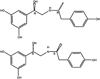
The main clinical manifestations of advanced chronic heart failure (CHF), e.g. in dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM), are reduced systolic and diastolic functions, increased arterial elastance and arterio-ventricular uncoupling, accompanied and exacerbated by an excessive sympathetic activation and extensive abnormalities in the βAR signaling. Loss of cardiomyocytes due to apoptosis is one mechanism that undoubtedly contributes to cardiac remodeling and functional deterioration associated with dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM). Research during the last decade on the single cardiomyocyte level strongly suggested that selective stimulation of β(1) AR activates the proapoptotic signaling pathways, while selective stimulation of β(2) AR is antiapoptotic, but its precise mechanisms remain to be elucidated. Extensive research in the rat model of DCM following induction of myocardial infarction (MI) showed that prolonged treatment with of β(2) AR agonist, fenoterol, in combination with a β(1) AR blocker, metoprolol, is more effective than β(1) AR blocker alone and as effective as β(1) AR blocker with ACE inhibitor with respect to survival and cardiac remodeling. This combined regimen of β(2) AR agonists and a β(1) AR blocker might be considered for clinical testing as alternative or adjunct therapy to currently acceptable CHF arsenal. This article is part of a special issue entitled "Key Signaling Molecules in Hypertrophy and Heart Failure."
Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- Lefkowitz RJ. The superfamily of heptahelical receptors. Nature Cell Biol. 2000;2:E133–E136. - PubMed
-
- Giembycz MA, Newton R. Beyond the dogma: novel beta2-adrenoceptor signalling in the airways. Eur Respir J. 2006;27:1286–12306. Review. - PubMed
-
- Lynch GS, Ryall JG. Role of beta-adrenoceptor signaling in skeletal muscle: implications for muscle wasting and disease. Physiol Rev. 2008;88:729–767. Review. - PubMed
-
- Hon JK, Yacoub MH. Bridge to recovery with the use of left ventricular assist device and clenbuterol. Ann Thorac Surg. 2003;75 Suppl:S36–S41. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

