Plk3 functions as an essential component of the hypoxia regulatory pathway by direct phosphorylation of HIF-1alpha
- PMID: 20889502
- PMCID: PMC2998109
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.160325
Plk3 functions as an essential component of the hypoxia regulatory pathway by direct phosphorylation of HIF-1alpha
Abstract
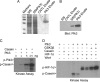
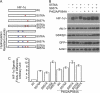
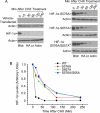
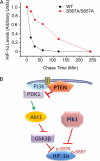
Polo-like kinase 3 (Plk3) plays an important role in the regulation of cell cycle progression and stress responses. Plk3 also has a tumor-suppressing activity as aging PLK3-null mice develop tumors in multiple organs. The growth of highly vascularized tumors in PLK3-null mice suggests a role for Plk3 in angiogenesis and cellular responses to hypoxia. By studying primary isogenic murine embryonic fibroblasts, we tested the hypothesis that Plk3 functions as a component in the hypoxia signaling pathway. PLK3(-/-) murine embryonic fibroblasts contained an enhanced level of HIF-1α under hypoxic conditions. Immunoprecipitation and pulldown analyses revealed that Plk3 physically interacted with HIF-1α under hypoxia. Purified recombinant Plk3, but not a kinase-defective mutant, phosphorylated HIF-1α in vitro, resulting in a major mobility shift. Mass spectrometry identified two unique serine residues that were phosphorylated by Plk3. Moreover, ectopic expression followed by cycloheximide or pulse-chase treatment demonstrated that phospho-mutants exhibited a much longer half-life than the wild-type counterpart, strongly suggesting that Plk3 directly regulates HIF-1α stability in vivo. Combined, our study identifies Plk3 as a new and essential player in the regulation of the hypoxia signaling pathway.
Figures


References
-
- Barr F. A., Silljé H. H., Nigg E. A. (2004) Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 5, 429–440 - PubMed
-
- Dai W. (2005) Oncogene 24, 214–216 - PubMed
-
- Zimmerman W. C., Erikson R. L. (2007) Cell Cycle 6, 1314–1318 - PubMed
-
- Xie S., Wang Q., Wu H., Cogswell J., Lu L., Jhanwar-Uniyal M., Dai W. (2001) J. Biol. Chem. 276, 36194–36199 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

