Induction of interleukin-6 expression by bone morphogenetic protein-6 in macrophages requires both SMAD and p38 signaling pathways
- PMID: 20889504
- PMCID: PMC2998138
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.103705
Induction of interleukin-6 expression by bone morphogenetic protein-6 in macrophages requires both SMAD and p38 signaling pathways
Abstract
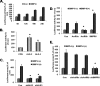
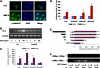
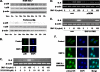
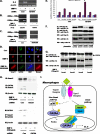
Unlike the prototype transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β), bone morphogenetic protein-6 (BMP-6) activates macrophages. Here, we report that BMP-6 induces the expression of IL-6 in macrophages. Using overexpression and knockdown experiments, we demonstrate that BMP receptor type II and activin-like kinase-2 are necessary for IL-6 induction by BMP-6. At the intracellular level, both Smad and p38 signaling pathways are required for the induction of IL-6. The cross-talk between the two pathways occurs at the level of transcription factor GATA4 and Smad 1/4. These results, taken together, demonstrate a novel BMP-6 signaling mechanism in which both the Smad and non-Smad pathways directly interact to activate the transcription of a target gene.
Figures

References
-
- Wozney J. M., Rosen V., Celeste A. J., Mitsock L. M., Whitters M. J., Kriz R. W., Hewick R. M., Wang E. A. (1988) Science 242, 1528–1534 - PubMed
-
- Zhao G. Q. (2003) Genesis 35, 43–56 - PubMed
-
- Miyazono K., Maeda S., Imamura T. (2005) Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 16, 251–263 - PubMed
-
- Kretzschmar M., Massagué J. (1998) Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 8, 103–111 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

