Anti-inflammatory effects of the neurotransmitter agonist Honokiol in a mouse model of allergic asthma
- PMID: 20889543
- PMCID: PMC3197781
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1000630
Anti-inflammatory effects of the neurotransmitter agonist Honokiol in a mouse model of allergic asthma
Abstract
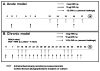
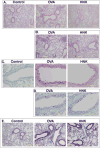
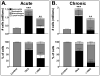
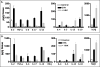
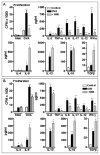
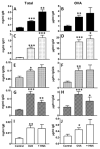
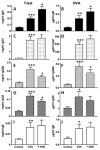
Chronic airway inflammation is a hallmark of asthma, an immune-based disease with great societal impact. Honokiol (HNK), a phenolic neurotransmitter receptor (γ-aminobutyric acid type A) agonist purified from magnolia, has anti-inflammatory properties, including stabilization of inflammation in experimentally induced arthritis. The present study tested the prediction that HNK could inhibit the chronic inflammatory component of allergic asthma. C57BL/6 mice sensitized to and challenged with OVA had increased airway hyperresponsiveness to methacholine challenge and eosinophilia compared with naive controls. HNK-treated mice showed a reduction in airway hyperresponsiveness as well as a significant decrease in lung eosinophilia. Histopathology studies revealed a marked drop in lung inflammation, goblet cell hyperplasia, and collagen deposition with HNK treatment. Ag recall responses from HNK-treated mice showed decreased proinflammatory cytokines in response to OVA, including TNF-α-, IL-6-, Th1-, and Th17-type cytokines, despite an increase in Th2-type cytokines. Regulatory cytokines IL-10 and TGF-β were also increased. Assessment of lung homogenates revealed a similar pattern of cytokines, with a noted increase in the number of FoxP3(+) cells in the lung. HNK was able to alter B and T lymphocyte cytokine secretion in a γ-aminobutyric acid type A-dependent manner. These results indicate that symptoms and pathology of asthma can be alleviated even in the presence of increased Th2 cytokines and that neurotransmitter agonists such as HNK have promise as a novel class of anti-inflammatory agents in the treatment of chronic asthma.
Figures
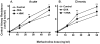

Similar articles
-
Anti-asthmatic effect of schizandrin on OVA-induced airway inflammation in a murine asthma model.Int Immunopharmacol. 2010 Nov;10(11):1374-9. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2010.07.014. Epub 2010 Aug 20. Int Immunopharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20727999
-
Oral administration of honokiol attenuates airway inflammation in asthmatic mouse model.Pak J Pharm Sci. 2018 Jul;31(4):1279-1284. Pak J Pharm Sci. 2018. PMID: 30033411
-
Honokiol, a natural plant product, inhibits inflammatory signals and alleviates inflammatory arthritis.J Immunol. 2007 Jul 15;179(2):753-63. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.179.2.753. J Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17617564
-
Microbes little helpers and suppliers for therapeutic asthma approaches.Respir Res. 2024 Jan 13;25(1):29. doi: 10.1186/s12931-023-02660-7. Respir Res. 2024. PMID: 38218816 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacological features, health benefits and clinical implications of honokiol.J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2023 Sep-Oct;41(15):7511-7533. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2022.2120541. Epub 2022 Sep 12. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2023. PMID: 36093963 Review.
Cited by
-
CaMKII is essential for the proasthmatic effects of oxidation.Sci Transl Med. 2013 Jul 24;5(195):195ra97. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3006135. Sci Transl Med. 2013. PMID: 23884469 Free PMC article.
-
Paeoniflorin inhibits human gastric carcinoma cell proliferation through up-regulation of microRNA-124 and suppression of PI3K/Akt and STAT3 signaling.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Jun 21;21(23):7197-207. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i23.7197. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 26109806 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of honokiol on cytochrome P450 and UDP-glucuronosyltransferase enzyme activities in human liver microsomes.Molecules. 2013 Sep 3;18(9):10681-93. doi: 10.3390/molecules180910681. Molecules. 2013. PMID: 24005963 Free PMC article.
-
Optimization of substituted imidazobenzodiazepines as novel asthma treatments.Eur J Med Chem. 2017 Jan 27;126:550-560. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2016.11.045. Epub 2016 Nov 24. Eur J Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 27915170 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial metabolites of diet-derived lignans and isoflavones inversely associate with asthma and wheezing.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015 Jan;135(1):267-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2014.07.035. Epub 2014 Sep 1. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25190319 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Busse WW, Lemanske RF., Jr Asthma. New England Journal of Medicine. 2001;344:350. - PubMed
-
- Chanez P, Wenzel SE, Anderson GP, Anto JM, Bel EH, Boulet LP, Brightling CE, Busse WW, Castro M, Dahlen B, Dahlen SE, Fabbri LM, Holgate ST, Humbert M, Gaga M, Joos GF, Levy B, Rabe KF, Sterk PJ, Wilson SJ, Vachier I. Severe asthma in adults: what are the important questions? Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology. 2007;119:1337. - PubMed
-
- Akdis M, Akdis CA. Therapeutic manipulation of immune tolerance in allergic disease. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery. 2009;8:645. - PubMed
-
- Nakajima H, Takatsu K. Role of cytokines in allergic airway inflammation. International Archives of Allergy and Immunology. 2007;142:265. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

