Apoptotic cells activate NKT cells through T cell Ig-like mucin-like-1 resulting in airway hyperreactivity
- PMID: 20889552
- PMCID: PMC3114419
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1001116
Apoptotic cells activate NKT cells through T cell Ig-like mucin-like-1 resulting in airway hyperreactivity
Abstract
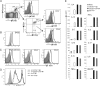
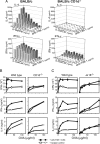
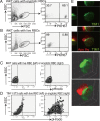
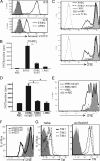
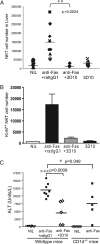
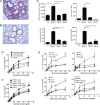
T cell Ig-like mucin-like-1 (TIM-1) is an important asthma susceptibility gene, but the immunological mechanisms by which TIM-1 functions remain uncertain. TIM-1 is also a receptor for phosphatidylserine (PtdSer), an important marker of cells undergoing programmed cell death, or apoptosis. We now demonstrate that NKT cells constitutively express TIM-1 and become activated by apoptotic cells expressing PtdSer. TIM-1 recognition of PtdSer induced NKT cell activation, proliferation, and cytokine production. Moreover, the induction of apoptosis in airway epithelial cells activated pulmonary NKT cells and unexpectedly resulted in airway hyperreactivity, a cardinal feature of asthma, in an NKT cell-dependent and TIM-1-dependent fashion. These results suggest that TIM-1 serves as a pattern recognition receptor on NKT cells that senses PtdSer on apoptotic cells as a damage-associated molecular pattern. Furthermore, these results provide evidence for a novel innate pathway that results in airway hyperreactivity and may help to explain how TIM-1 and NKT cells regulate asthma.
Figures
Similar articles
-
T-cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain 1 deficiency eliminates airway hyperreactivity triggered by the recognition of airway cell death.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013 Aug;132(2):414-25.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2013.03.025. Epub 2013 May 11. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23672783 Free PMC article.
-
T cell/transmembrane, Ig, and mucin-3 allelic variants differentially recognize phosphatidylserine and mediate phagocytosis of apoptotic cells.J Immunol. 2010 Feb 15;184(4):1918-30. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0903059. Epub 2010 Jan 18. J Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20083673 Free PMC article.
-
An important role of tumor necrosis factor receptor-2 on natural killer T cells on the development of dsRNA-enhanced Th2 cell response to inhaled allergens.Allergy. 2014 Feb;69(2):186-98. doi: 10.1111/all.12301. Epub 2013 Nov 6. Allergy. 2014. PMID: 24191851
-
Novel roles for TIM-1 in immunity and infection.Immunol Lett. 2011 Dec 30;141(1):28-35. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2011.08.003. Epub 2011 Sep 2. Immunol Lett. 2011. PMID: 21911007 Review.
-
TIM genes: a family of cell surface phosphatidylserine receptors that regulate innate and adaptive immunity.Immunol Rev. 2010 May;235(1):172-89. doi: 10.1111/j.0105-2896.2010.00903.x. Immunol Rev. 2010. PMID: 20536563 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
TIM-4 is expressed on invariant NKT cells but dispensable for their development and function.Oncotarget. 2016 Nov 1;7(44):71099-71111. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12153. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27662666 Free PMC article.
-
The role of phosphatidylserine on the membrane in immunity and blood coagulation.Biomark Res. 2022 Jan 15;10(1):4. doi: 10.1186/s40364-021-00346-0. Biomark Res. 2022. PMID: 35033201 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of CD1d- and MR1-Restricted T Cells in Asthma.Front Immunol. 2018 Aug 28;9:1942. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01942. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30210497 Free PMC article. Review.
-
T-cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain 1 deficiency eliminates airway hyperreactivity triggered by the recognition of airway cell death.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013 Aug;132(2):414-25.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2013.03.025. Epub 2013 May 11. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23672783 Free PMC article.
-
Immune Regulation and Antitumor Effect of TIM-1.J Immunol Res. 2016;2016:8605134. doi: 10.1155/2016/8605134. Epub 2016 Jun 20. J Immunol Res. 2016. PMID: 27413764 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- McIntire JJ, Umetsu SE, Macaubas C, Hoyte EG, Cinnioglu C, Cavalli-Sforza LL, Barsh GS, Hallmayer JF, Underhill PA, Risch NJ, et al. Immunology: hepatitis A virus link to atopic disease. Nature. 2003;425:576. - PubMed
-
- Chae SC, Song JH, Shim SC, Yoon KS, Chung HT. The exon 4 variations of Tim-1 gene are associated with rheumatoid arthritis in a Korean population. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004;315:971–975. - PubMed
-
- McIntire JJ, Umetsu SE, Akbari O, Potter M, Kuchroo VK, Barsh GS, Freeman GJ, Umetsu DT, DeKruyff RH. Identification of Tapr (an airway hyperreactivity regulatory locus) and the linked Tim gene family. Nat. Immunol. 2001;2:1109–1116. - PubMed
-
- Umetsu SE, Lee WL, McIntire JJ, Downey L, Sanjanwala B, Akbari O, Berry GJ, Nagumo H, Freeman GJ, Umetsu DT, DeKruyff RH. TIM-1 induces T cell activation and inhibits the development of peripheral tolerance. Nat. Immunol. 2005;6:447–454. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- T32 AI007290/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01AI02632/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI026322/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- RC1 HL099839/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL062348/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI054456/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01AI05546/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI089955/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK034854/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK-034854/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL62348/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI083523/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

