Hypermethylation of PTGER2 confers prostaglandin E2 resistance in fibrotic fibroblasts from humans and mice
- PMID: 20889571
- PMCID: PMC2966784
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2010.100446
Hypermethylation of PTGER2 confers prostaglandin E2 resistance in fibrotic fibroblasts from humans and mice
Abstract
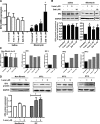
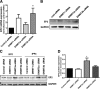
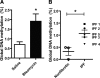
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a devastating lung disease that is characterized by excessive proliferation of fibroblasts. The lipid mediator prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) has the capacity to limit fibrosis through its inhibition of numerous functions of these fibroblasts; however, in the setting of fibrosis, fibroblasts have been shown to be resistant to PGE2. We have linked such resistance to decreased expression levels of the E prostanoid 2 (EP2) receptor. In this study, in fibroblasts from both mice and humans with pulmonary fibrosis, we show that DNA hypermethylation is responsible for diminished EP2 expression levels and PGE2 resistance. Bisulfite sequencing of the prostaglandin E receptor 2 gene (PTGER2) promoter revealed that fibrotic fibroblasts exhibit greater PTGER2 methylation than nonfibrotic control cells. Treatment with the DNA methylation inhibitors 5-aza-2'-deoxycytidine and zebularine as well as DNA methyltransferase-specific siRNA decreased PTGER2 methylation, increased EP2 mRNA and protein expression levels, and restored PGE2 responsiveness in fibrotic fibroblasts but not in nonfibrotic controls. PTGER2 promoter hypermethylation was driven by an increase in Akt signal transduction. In addition to results described for the PTGER2 promoter, fibrotic fibroblasts also exhibited increased global DNA methylation. These findings demonstrate that the down-regulation of PTGER2 and consequent PGE2 resistance are both mediated by DNA hypermethylation; we identified increased Akt signal transduction as a novel mechanism that promotes DNA hypermethylation during fibrogenesis.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Microsomal prostaglandin E synthase-1 deficiency exacerbates pulmonary fibrosis induced by bleomycin in mice.Molecules. 2014 Apr 21;19(4):4967-85. doi: 10.3390/molecules19044967. Molecules. 2014. PMID: 24756129 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic regulation of cyclooxygenase-2 by methylation of c8orf4 in pulmonary fibrosis.Clin Sci (Lond). 2016 Apr;130(8):575-86. doi: 10.1042/CS20150697. Epub 2016 Jan 7. Clin Sci (Lond). 2016. PMID: 26744410 Free PMC article.
-
Impaired E Prostanoid2 Expression and Resistance to Prostaglandin E2 in Nasal Polyp Fibroblasts from Subjects with Aspirin-Exacerbated Respiratory Disease.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2016 Jan;54(1):34-40. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2014-0486OC. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 26051534 Free PMC article.
-
Prostaglandin E2 inhibits profibrotic function of human pulmonary fibroblasts by disrupting Ca2+ signaling.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2019 May 1;316(5):L810-L821. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00403.2018. Epub 2019 Feb 13. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30758990 Free PMC article.
-
Prostaglandin receptor EP2 in the crosshairs of anti-inflammation, anti-cancer, and neuroprotection.Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2013 Jul;34(7):413-23. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2013.05.003. Epub 2013 Jun 21. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23796953 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Epigenetics within the matrix: a neo-regulator of fibrotic disease.Epigenetics. 2012 Sep;7(9):987-93. doi: 10.4161/epi.21567. Epub 2012 Aug 16. Epigenetics. 2012. PMID: 22894907 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reversal of myofibroblast differentiation by prostaglandin E(2).Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2013 May;48(5):550-8. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2012-0262OC. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23470625 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of immune responses by prostaglandin E2.J Immunol. 2012 Jan 1;188(1):21-8. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1101029. J Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22187483 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptomic changes involved in the dedifferentiation of myofibroblasts derived from the lung of a patient with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.Mol Med Rep. 2020 Aug;22(2):1518-1526. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2020.11218. Epub 2020 Jun 10. Mol Med Rep. 2020. PMID: 32626975 Free PMC article.
-
Matrix metalloproteinase-19 is a key regulator of lung fibrosis in mice and humans.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2012 Oct 15;186(8):752-62. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201202-0302OC. Epub 2012 Aug 2. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2012. PMID: 22859522 Free PMC article.
References
-
- American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society International Multidisciplinary Consensus Classification of the Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias. This joint statement of the American Thoracic Society (ATS), and the European Respiratory Society (ERS) was adopted by the ATS board of directors, June 2001 and by the ERS Executive Committee, June 2001. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002;165:277–304. - PubMed
-
- Gross TJ, Hunninghake GW. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:517–525. - PubMed
-
- Katzenstein AL. Katzenstein AL, editor. Philadelphia: Saunders,; Katzenstein and Askin’s Surgical Pathology of Non-Neoplastic Lung Disease, (4th Edition.) 2006:236–260.
-
- Kuhn C, 3rd, Boldt J, King TE, Jr, Crouch E, Vartio T, McDonald JA. An immunohistochemical study of architectural remodeling and connective tissue synthesis in pulmonary fibrosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989;140:1693–1703. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

