Gibberellins control fruit patterning in Arabidopsis thaliana
- PMID: 20889713
- PMCID: PMC2947765
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.593410
Gibberellins control fruit patterning in Arabidopsis thaliana
Abstract
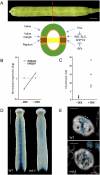
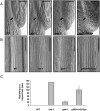
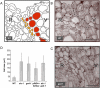
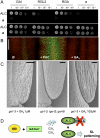
The Arabidopsis basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) proteins INDEHISCENT (IND) and ALCATRAZ (ALC) specify tissues required for fruit opening that have major roles in seed dispersal and plant domestication. Here, we show that synthesis of the phytohormone gibberellin is a direct and necessary target of IND, and that ALC interacts directly with DELLA repressors, which antagonize ALC function but are destabilized by gibberellin. Thus, the gibberellin/DELLA pathway has a key role in patterning the Arabidopsis fruit, and the interaction between DELLA and bHLH proteins, previously shown to connect gibberellin and light responses, is a versatile regulatory module also used in tissue patterning.
Figures
References
-
- Bangi E, Wharton K 2006. Dpp and Gbb exhibit different effective ranges in the establishment of the BMP activity gradient critical for Drosophila wing patterning. Dev Biol 295: 178–193 - PubMed
-
- Bruce DM, Farrent JW, Morgan CL, Child RD 2002. Determining the oilseed rape pod strength needed to reduce seed loss due to pod shatter. Biosys Eng 81: 179–184
-
- de Lucas M, Daviere JM, Rodriguez-Falcon M, Pontin M, Iglesias-Pedraz JM, Lorrain S, Fankhauser C, Blazquez MA, Titarenko E, Prat S 2008. A molecular framework for light and gibberellin control of cell elongation. Nature 451: 480–484 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- BB/D018005/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/E024807/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BBS/E/J/00000613/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BBS/E/J/000CA382/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
