TULP3 bridges the IFT-A complex and membrane phosphoinositides to promote trafficking of G protein-coupled receptors into primary cilia
- PMID: 20889716
- PMCID: PMC2947770
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1966210
TULP3 bridges the IFT-A complex and membrane phosphoinositides to promote trafficking of G protein-coupled receptors into primary cilia
Abstract
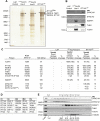
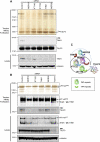
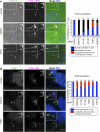
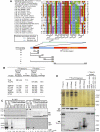
Primary cilia function as a sensory signaling compartment in processes ranging from mammalian Hedgehog signaling to neuronal control of obesity. Intraflagellar transport (IFT) is an ancient, conserved mechanism required to assemble cilia and for trafficking within cilia. The link between IFT, sensory signaling, and obesity is not clearly defined, but some novel monogenic obesity disorders may be linked to ciliary defects. The tubby mouse, which presents with adult-onset obesity, arises from mutation in the Tub gene. The tubby-like proteins comprise a related family of poorly understood proteins with roles in neural development and function. We find that specific Tubby family proteins, notably Tubby-like protein 3 (TULP3), bind to the IFT-A complex. IFT-A is linked to retrograde ciliary transport, but, surprisingly, we find that the IFT-A complex has a second role directing ciliary entry of TULP3. TULP3 and IFT-A, in turn, promote trafficking of a subset of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), but not Smoothened, to cilia. Both IFT-A and membrane phosphoinositide-binding properties of TULP3 are required for ciliary GPCR localization. TULP3 and IFT-A proteins both negatively regulate Hedgehog signaling in the mouse embryo, and the TULP3-IFT-A interaction suggests how these proteins cooperate during neural tube patterning.
Figures
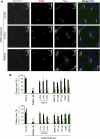
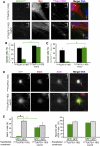

References
-
- Bishop GA, Berbari NF, Lewis J, Mykytyn K 2007. Type III adenylyl cyclase localizes to primary cilia throughout the adult mouse brain. J Comp Neurol 505: 562–571 - PubMed
-
- Boggon TJ, Shan WS, Santagata S, Myers SC, Shapiro L 1999. Implication of tubby proteins as transcription factors by structure-based functional analysis. Science 286: 2119–2125 - PubMed
-
- Cameron DA, Pennimpede T, Petkovich M 2009. Tulp3 is a critical repressor of mouse hedgehog signaling. Dev Dyn 238: 1140–1149 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
