The protein phosphatase 1 regulator PNUTS is a new component of the DNA damage response
- PMID: 20890310
- PMCID: PMC2966950
- DOI: 10.1038/embor.2010.134
The protein phosphatase 1 regulator PNUTS is a new component of the DNA damage response
Abstract
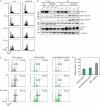
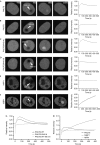
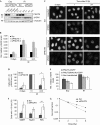
The function of protein phosphatase 1 nuclear-targeting subunit (PNUTS)--one of the most abundant nuclear-targeting subunits of protein phosphatase 1 (PP1c)--remains largely uncharacterized. We show that PNUTS depletion by small interfering RNA activates a G2 checkpoint in unperturbed cells and prolongs G2 checkpoint and Chk1 activation after ionizing-radiation-induced DNA damage. Overexpression of PNUTS-enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP)--which is rapidly and transiently recruited at DNA damage sites--inhibits G2 arrest. Finally, γH2AX, p53-binding protein 1, replication protein A and Rad51 foci are present for a prolonged period and clonogenic survival is decreased in PNUTS-depleted cells after ionizing radiation treatment. We identify the PP1c regulatory subunit PNUTS as a new and integral component of the DNA damage response involved in DNA repair.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Allen PB, Kwon YG, Nairn AC, Greengard P (1998) Isolation and characterization of PNUTS, a putative protein phosphatase 1 nuclear targeting subunit. J Biol Chem 273: 4089–4095 - PubMed
-
- Ayoub N, Jeyasekharan AD, Bernal JA, Venkitaraman AR (2008) HP1-beta mobilization promotes chromatin changes that initiate the DNA damage response. Nature 453: 682–686 - PubMed
-
- Bollen M, Gerlich DW, Lesage B (2009) Mitotic phosphatases: from entry guards to exit guides. Trends Cell Biol 19: 531–541 - PubMed
-
- De Leon G, Sherry TC, Krucher NA (2008) Reduced expression of PNUTS leads to activation of Rb-phosphatase- and caspase-mediated apoptosis. Cancer Biol Ther 7: 833–841 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

