Stem torsion in total hip replacement
- PMID: 20919811
- PMCID: PMC3214746
- DOI: 10.3109/17453674.2010.524596
Stem torsion in total hip replacement
Abstract
Background and purpose: The clinical results of THR may be improved by correct femoral torsion. We evaluated the stem position by postoperative CT examination in 60 patients.
Methods: 60 patients requiring total hip arthroplasty were prospectively enrolled in this study. Minimally invasive THR was performed (anterior approach) in a lateral decubitus position and each patient underwent a postoperative CT examination. The position of the stem was evaluated by an independent external institution.
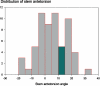
Results: Stem torsion ranged from – 19° retrotorsion to 33° antetorsion. Normal antetorsion (i.e 10–15° according to Tönnis) was present in 5 of 60 patients, so the prevalence of abnormal stem antetorsion was 92% (95% CI: 82–97). We found a stem antetorsion outside the range of 0–25° in 21 of 60 hips. Women had a higher mean stem antetorsion (8.0° (SD 11)) than men (1.5° (SD 10)).
Interpretation: Postoperative stem antetorsion shows a high variability and is gender-related. We suggest precise assessment of stem antetorsion intraoperatively by means of computer navigation, preparing the femur first. In abnormal stem antetorsion, the cup position can be adjusted using a combined anteversion concept; alternatively, modular femoral components or stems with retroverted or anteverted necks ("retrostem") could be used.
Figures

Comment in
-
Visual intraoperative estimation of cup and stem position is not reliable in minimally invasive hip arthroplasty.Acta Orthop. 2016 Jun;87(3):225-30. doi: 10.3109/17453674.2015.1137182. Epub 2016 Feb 5. Acta Orthop. 2016. PMID: 26848628 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anda S, Terjesen T, Kvistad KA, Svenningsen S. Acetabular angles and femoral anteversion in dysplastic hips in adults: CT investigation. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1991;15((1)):115–20. - PubMed
-
- Flecher X, Argenson JN, Parratte S, Ryembault E, Aubaniac JM. Custom cementless stem for osteoarthritis following developmental hip dysplasia. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot. 2006;92((4)):332–42. - PubMed
-
- Flecher X, Parratte S, Aubaniac JM, Argenson JN. Three-dimensional custom-designed cementless femoral stem for osteoarthritis secondary to congenital dislocation of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg (Br) 2007;89((12)):1586–91. - PubMed
-
- Husmann O, Rubin PJ, Leyvraz PF, de Roguin B, Argenson JN. Three-dimensional morphology of the proximal femur. J Arthroplasty. 1997;12((4)):444–50. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
