The dynamic interaction of AMBRA1 with the dynein motor complex regulates mammalian autophagy
- PMID: 20921139
- PMCID: PMC2953445
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.201002100
The dynamic interaction of AMBRA1 with the dynein motor complex regulates mammalian autophagy
Abstract
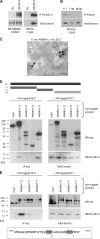
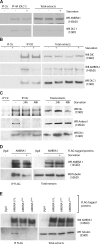
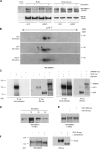
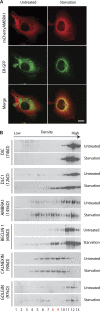
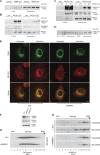
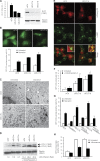
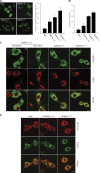
Autophagy is an evolutionary conserved catabolic process involved in several physiological and pathological processes such as cancer and neurodegeneration. Autophagy initiation signaling requires both the ULK1 kinase and the BECLIN 1-VPS34 core complex to generate autophagosomes, double-membraned vesicles that transfer cellular contents to lysosomes. In this study, we show that the BECLIN 1-VPS34 complex is tethered to the cytoskeleton through an interaction between the BECLIN 1-interacting protein AMBRA1 and dynein light chains 1/2. When autophagy is induced, ULK1 phosphorylates AMBRA1, releasing the autophagy core complex from dynein. Its subsequent relocalization to the endoplasmic reticulum enables autophagosome nucleation. Therefore, AMBRA1 constitutes a direct regulatory link between ULK1 and BECLIN 1-VPS34, which is required for core complex positioning and activity within the cell. Moreover, our results demonstrate that in addition to a function for microtubules in mediating autophagosome transport, there is a strict and regulatory relationship between cytoskeleton dynamics and autophagosome formation.
Figures

References
-
- Axe E.L., Walker S.A., Manifava M., Chandra P., Roderick H.L., Habermann A., Griffiths G., Ktistakis N.T. 2008. Autophagosome formation from membrane compartments enriched in phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate and dynamically connected to the endoplasmic reticulum. J. Cell Biol. 182:685–701 10.1083/jcb.200803137 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Campbell K.S., Cooper S., Dessing M., Yates S., Buder A. 1998. Interaction of p59fyn kinase with the dynein light chain, Tctex-1, and colocalization during cytokinesis. J. Immunol. 161:1728–1737 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

