MST1 promotes apoptosis through phosphorylation of histone H2AX
- PMID: 20921231
- PMCID: PMC2998151
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.151753
MST1 promotes apoptosis through phosphorylation of histone H2AX
Abstract
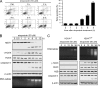
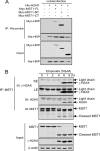
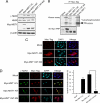
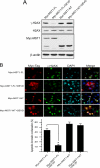
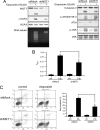
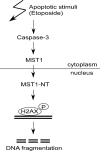
MST1 (mammalian STE20-like kinase 1) is a serine/threonine kinase that is cleaved and activated by caspases during apoptosis. Overexpression of MST1 induces apoptotic morphological changes such as chromatin condensation, but the mechanism is not clear. Here we show that MST1 induces apoptotic chromatin condensation through its phosphorylation of histone H2AX at Ser-139. During etoposide-induced apoptosis in Jurkat cells, the cleavage of MST1 directly corresponded with strong H2AX phosphorylation. In vitro kinase assay results showed that MST1 strongly phosphorylates histone H2AX. Western blot and kinase assay results with a mutant S139A H2AX confirmed that MST1 phosphorylates H2AX at Ser-139. Direct binding of MST1 and H2AX can be detected when co-expressed in HEK293 cells and was also confirmed by an endogenous immunoprecipitation study. When overexpressed in HeLa cells, both the MST1 full-length protein and the MST1 kinase domain (MST1-NT), but not the kinase-negative mutant (MST1-NT-KN), could induce obvious endogenous histone H2AX phosphorylation. The caspase-3 inhibitor benzyloxycarbonyl-DEVD-fluoromethyl ketone (Z-DEVD-fmk) attenuates phosphorylation of H2AX by MST1 but cannot inhibit MST1-NT-induced histone H2AX phosphorylation, indicating that cleaved MST1 is responsible for H2AX phosphorylation during apoptosis. Histone H2AX phosphorylation and DNA fragmentation were suppressed in MST1 knockdown Jurkat cells after etoposide treatment. Taken together, our data indicated that H2AX is a substrate of MST1, which functions to induce apoptotic chromatin condensation and DNA fragmentation.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Imatinib induces H2AX phosphorylation and apoptosis in chronic myelogenous leukemia cells in vitro via caspase-3/Mst1 pathway.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2012 Apr;33(4):551-7. doi: 10.1038/aps.2012.9. Epub 2012 Mar 5. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2012. PMID: 22388075 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of the c-Jun N-terminal kinase pathway by MST1 is essential and sufficient for the induction of chromatin condensation during apoptosis.Mol Cell Biol. 2007 Aug;27(15):5514-22. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00199-07. Epub 2007 Jun 4. Mol Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17548476 Free PMC article.
-
Apoptotic phosphorylation of histone H2B is mediated by mammalian sterile twenty kinase.Cell. 2003 May 16;113(4):507-17. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(03)00355-6. Cell. 2003. PMID: 12757711
-
MST1: a promising therapeutic target to restore functional beta cell mass in diabetes.Diabetologia. 2016 Sep;59(9):1843-9. doi: 10.1007/s00125-016-3892-9. Epub 2016 Apr 6. Diabetologia. 2016. PMID: 27053234 Review.
-
MST1/MST2 Protein Kinases: Regulation and Physiologic Roles.Biochemistry. 2016 Oct 4;55(39):5507-5519. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.6b00763. Epub 2016 Sep 26. Biochemistry. 2016. PMID: 27618557 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The SARAH Domain of RASSF1A and Its Tumor Suppressor Function.Mol Biol Int. 2012;2012:196715. doi: 10.1155/2012/196715. Epub 2012 Apr 9. Mol Biol Int. 2012. PMID: 22577552 Free PMC article.
-
The phenotype of human STK4 deficiency.Blood. 2012 Apr 12;119(15):3450-7. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-09-378158. Epub 2012 Jan 31. Blood. 2012. PMID: 22294732 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the YAP-1 Transcriptional Target cIAP2 in the Differential Susceptibility to Chemotherapy of Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Patients with Tumor RASSF1A Gene Methylation from the Phase 3 IFCT-0002 Trial.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Nov 21;11(12):1835. doi: 10.3390/cancers11121835. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31766357 Free PMC article.
-
Picrasidine I Triggers Heme Oxygenase-1-Induced Apoptosis in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Cells via ERK and Akt Signaling Pathways.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May 29;23(11):6103. doi: 10.3390/ijms23116103. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35682782 Free PMC article.
-
hMOB3 modulates MST1 apoptotic signaling and supports tumor growth in glioblastoma multiforme.Cancer Res. 2014 Jul 15;74(14):3779-89. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-3430. Epub 2014 May 28. Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 24872389 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

