Conservation of an RNA regulatory map between Drosophila and mammals
- PMID: 20921232
- PMCID: PMC3032923
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.108662.110
Conservation of an RNA regulatory map between Drosophila and mammals
Abstract
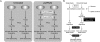
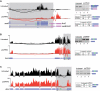
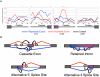
Alternative splicing is generally controlled by proteins that bind directly to regulatory sequence elements and either activate or repress splicing of adjacent splice sites in a target pre-mRNA. Here, we have combined RNAi and mRNA-seq to identify exons that are regulated by Pasilla (PS), the Drosophila melanogaster ortholog of mammalian NOVA1 and NOVA2. We identified 405 splicing events in 323 genes that are significantly affected upon depletion of ps, many of which were annotated as being constitutively spliced. The sequence regions upstream and within PS-repressed exons and downstream from PS-activated exons are enriched for YCAY repeats, and these are consistent with the location of these motifs near NOVA-regulated exons in mammals. Thus, the RNA regulatory map of PS and NOVA1/2 is highly conserved between insects and mammals despite the fact that the target gene orthologs regulated by PS and NOVA1/2 are almost entirely nonoverlapping. This observation suggests that the regulatory codes of individual RNA binding proteins may be nearly immutable, yet the regulatory modules controlled by these proteins are highly evolvable.
Figures

References
-
- Adams MD, Celniker SE, Holt RA, Evans CA, Gocayne JD, Amanatides PG, Scherer SE, Li PW, Hoskins RA, Galle RF, et al. 2000. The genome sequence of Drosophila melanogaster. Science 287: 2185–2195 - PubMed
-
- Barash Y, Calarco JA, Gao W, Pan Q, Wang X, Shai O, Blencowe BJ, Frey BJ 2010. Deciphering the splicing code. Nature 465: 53–59 - PubMed
-
- Blanchette M, Labourier E, Green RE, Brenner SE, Rio DC 2004. Genome-wide analysis reveals an unexpected function for the Drosophila splicing factor U2AF50 in the nuclear export of intronless mRNAs. Mol Cell 14: 775–786 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
