Tigecycline population pharmacokinetics in patients with community- or hospital-acquired pneumonia
- PMID: 20921315
- PMCID: PMC2981274
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.01414-09
Tigecycline population pharmacokinetics in patients with community- or hospital-acquired pneumonia
Abstract
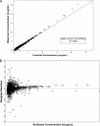
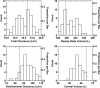
Tigecycline is a new-generation of tetracycline (glycylcyclines) and is active in vitro against bacteria that possess any of the classical genes that confer tetracycline resistance through ribosomal protection or efflux pumps. Herein, tigecycline disposition in patients with community- or hospital-acquired pneumonia was described using a population pharmacokinetic model. Additionally, the influence of covariates, such as body surface area, severity of illness, and clinical laboratory measures, on tigecycline disposition was evaluated. An intravenous loading dose of 100 mg was followed by 50 mg of tigecycline every 12 h. The final population pharmacokinetic model was a two-compartment model with linear elimination and with a relationship between tigecycline clearance and body surface area and creatinine clearance. The model was parameterized using total clearance (CL), the volume of the central compartment, distributional clearance from the central to the peripheral compartment, and volumes of distribution at steady state. Relationships between body surface area and creatinine clearance were identified as significant predictors of interindividual variability on CL. This model will serve as the basis for estimating tigecycline exposure for pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic analyses for efficacy and safety among patients with community- or hospital-acquired pneumonia.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pharmacological and patient-specific response determinants in patients with hospital-acquired pneumonia treated with tigecycline.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012 Feb;56(2):1065-72. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01615-10. Epub 2011 Dec 5. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012. PMID: 22143524 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Population Pharmacokinetics of Tigecycline in Critically Ill Patients with Severe Infections.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017 Jul 25;61(8):e00345-17. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00345-17. Print 2017 Aug. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017. PMID: 28607024 Free PMC article.
-
Population pharmacokinetics of tigecycline in patients with complicated intra-abdominal or skin and skin structure infections.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006 Nov;50(11):3701-7. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01636-05. Epub 2006 Aug 28. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006. PMID: 16940069 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Tigecycline: in community-acquired pneumonia.Drugs. 2008;68(18):2633-44. doi: 10.2165/0003495-200868180-00008. Drugs. 2008. PMID: 19093704 Review.
-
The glycylcyclines: a comparative review with the tetracyclines.Drugs. 2004;64(1):63-88. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200464010-00005. Drugs. 2004. PMID: 14723559 Review.
Cited by
-
Establishment and Validation of a Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry Method for the Determination of Tigecycline in Critically Ill Patients.Int J Anal Chem. 2020 Dec 29;2020:6671392. doi: 10.1155/2020/6671392. eCollection 2020. Int J Anal Chem. 2020. PMID: 33456470 Free PMC article.
-
Potential role of tigecycline in the treatment of community-acquired bacterial pneumonia.Infect Drug Resist. 2011;4:77-86. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S6030. Epub 2011 Mar 2. Infect Drug Resist. 2011. PMID: 21694911 Free PMC article.
-
The Monte Carlo Simulation of Three Antimicrobials for Empiric Treatment of Adult Bloodstream Infections With Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacterales in China.Front Microbiol. 2021 Nov 25;12:738812. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.738812. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34899628 Free PMC article.
-
Population Pharmacokinetics of High-Dose Tigecycline in Patients with Sepsis or Septic Shock.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2018 Mar 27;62(4):e02273-17. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02273-17. Print 2018 Apr. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2018. PMID: 29358291 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological and patient-specific response determinants in patients with hospital-acquired pneumonia treated with tigecycline.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012 Feb;56(2):1065-72. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01615-10. Epub 2011 Dec 5. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012. PMID: 22143524 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Akaike, H. 1979. A Bayesian extension of the minimum AIC procedure of autoregressive model fitting. Biometrika 66:237-242.
-
- Ambrose, P. G., S. M. Bhavnani, C. M. Rubino, A. Louie, T. Gumbo, A. Forrest, and G. L. Drusano. 2007. Pharmacokinetics-pharmacodynamics of antimicrobial therapy: It's not just for mice anymore. Clin. Infect. Dis. 44:79-86. - PubMed
-
- Bassett, E. J., M. S. Keith, G. J. Armelagos, D. L. Martin, and A. R. Villnueva. 1980. Tetracycline labeled human bone from ancient Sudanese Nubia. Science 209:1532-1534. - PubMed
-
- Bauer, R. J. 2006. S-ADAPT/MCPEM user's guide: software for pharmacokinetic, pharmacodynamic and population data analysis. Biomedical Simulations Resource, Los Angeles, CA. http://bmsr.usc.edu/Software/ADAPT/SADAPTsoftware.html.
-
- Beal, S. 2001. Ways to fit a PK model with some data below the quantification limit. J. Pharmacokinet. Pharmacodyn. 2:481-504. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

