Novel daptomycin combinations against daptomycin-nonsusceptible methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in an in vitro model of simulated endocardial vegetations
- PMID: 20921318
- PMCID: PMC2981245
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00536-10
Novel daptomycin combinations against daptomycin-nonsusceptible methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in an in vitro model of simulated endocardial vegetations
Abstract
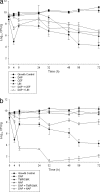
Reduced susceptibility to daptomycin has been reported in patients with infections due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Although infections with daptomycin-nonsusceptible (DNS) MRSA are infrequent, optimal therapy of these strains has not been determined. We investigated the killing effects of novel antibiotic combinations with daptomycin (DAP) against two clinical DNS MRSA isolates (SA-684 and R6003) in a 72-h in vitro pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic (PK/PD) model with simulated endocardial vegetations (SEV). Simulated regimens included DAP at 6 mg/kg every 24 h (q24h) alone or in combination with trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (TMP/SMX) at 160/800 mg q12h, linezolid (LIN) at 600 mg q12h, cefepime (CEF) at 2 g q12h, and nafcillin (NAF) at 4 g q4h. Bactericidal activity was defined as a ≥3-log(10) CFU/g kill. Differences in CFU/g were evaluated between 4 and 72 h by analysis of variance with the Bonferroni post hoc test. DAP MICs were 4 and 2 mg/liter for SA-684 and R6003, respectively. In the PK/PD model, DAP alone was slowly bactericidal, achieving a 3-log(10) kill at 24 and 50 h for SA-684 and R6003, respectively. Against SA-684, DAP plus TMP/SMX, CEF, LIN, or NAF was bactericidal at 4, 4, 8, and 8 h, respectively, and maintained this activity for the 72-h study duration. DAP plus TMP/SMX or CEF exhibited superior killing than DAP alone against SA-684 between 4 and 72 h, and overall this was significant (P < 0.05). Against R6003, DAP plus TMP/SMX was bactericidal (8 h) and superior to DAP alone between 8 and 72 h (P < 0.001). The unique combination of DAP plus TMP/SMX was the most effective and rapidly bactericidal regimen against the two isolates tested and may provide a clinical option to treat DNS S. aureus infections.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Evaluation of the novel combination of high-dose daptomycin plus trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole against daptomycin-nonsusceptible methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus using an in vitro pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic model of simulated endocardial vegetations.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012 Nov;56(11):5709-14. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01185-12. Epub 2012 Aug 20. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012. PMID: 22908167 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of ceftaroline, vancomycin, daptomycin, or ceftaroline plus daptomycin against daptomycin-nonsusceptible methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in an in vitro pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic model of simulated endocardial vegetations.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014 Jun;58(6):3177-81. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00088-14. Epub 2014 Mar 24. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014. PMID: 24663016 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of telavancin activity versus daptomycin and vancomycin against daptomycin-nonsusceptible Staphylococcus aureus in an in vitro pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic model.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012 Feb;56(2):955-9. doi: 10.1128/AAC.05849-11. Epub 2011 Nov 28. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012. PMID: 22123693 Free PMC article.
-
Pre-clinical Impact of the Synergistic Mechanism of Daptomycin and Ceftaroline on Patients with Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus Bacteremia Infections.Curr Rev Clin Exp Pharmacol. 2021;16(4):296-299. doi: 10.2174/1574884715666210108103813. Curr Rev Clin Exp Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33423652 Review.
-
Vancomycin, Daptomycin, Antistaphylococcal β-Lactam, and Trimethoprim-Sulfamethoxazole Monotherapy and Combination Therapy in the Management of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus: A Network Meta-Analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2022 May 17;13:805966. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.805966. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35656305 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Ceftaroline increases membrane binding and enhances the activity of daptomycin against daptomycin-nonsusceptible vancomycin-intermediate Staphylococcus aureus in a pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic model.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013 Jan;57(1):66-73. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01586-12. Epub 2012 Oct 15. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013. PMID: 23070161 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship of in vitro synergy and treatment outcome with daptomycin plus rifampin in patients with invasive methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013 Jul;57(7):3450-2. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00325-12. Epub 2013 May 6. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013. PMID: 23650174 Free PMC article.
-
β-Lactams increase the antibacterial activity of daptomycin against clinical methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains and prevent selection of daptomycin-resistant derivatives.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012 Dec;56(12):6192-200. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01525-12. Epub 2012 Sep 17. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012. PMID: 22985884 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative efficacies of cloxacillin-daptomycin and the standard cloxacillin-rifampin therapies against an experimental foreign-body infection by methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014 Sep;58(9):5576-80. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02681-14. Epub 2014 Jun 23. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014. PMID: 24957833 Free PMC article.
-
A study on combination of daptomycin with selected antimicrobial agents: in vitro synergistic effect of MIC value of 1 mg/L against MRSA strains.BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2019 May 6;20(1):25. doi: 10.1186/s40360-019-0305-y. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2019. PMID: 31060599 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akins, R. L., and M. J. Rybak. 2001. Bactericidal activities of two daptomycin regimens against clinical strains of glycopeptide intermediate-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecium, and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates in an in vitro pharmacodynamic model with simulated endocardial vegetations. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 45:454-459. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Allen, G. P., R. Cha, and M. J. Rybak. 2002. In vitro activities of quinupristin-dalfopristin and cefepime, alone and in combination with various antimicrobials, against multidrug-resistant staphylococci and enterococci in an in vitro pharmacodynamic model. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 46:2606-2612. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Blaser, J. 1985. In-vitro model for simultaneous simulation of the serum kinetics of two drugs with different half-lives. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 15(Suppl. A):125-130. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

