Genome-wide analysis reveals methyl-CpG-binding protein 2-dependent regulation of microRNAs in a mouse model of Rett syndrome
- PMID: 20921386
- PMCID: PMC2964235
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1005595107
Genome-wide analysis reveals methyl-CpG-binding protein 2-dependent regulation of microRNAs in a mouse model of Rett syndrome
Abstract
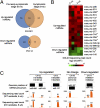
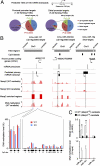
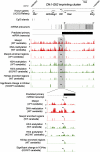
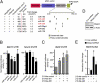
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are a class of small, noncoding RNAs that function as posttranscriptional regulators of gene expression. Many miRNAs are expressed in the developing brain and regulate multiple aspects of neural development, including neurogenesis, dendritogenesis, and synapse formation. Rett syndrome (RTT) is a progressive neurodevelopmental disorder caused by mutations in the gene encoding methyl-CpG-binding protein 2 (MECP2). Although Mecp2 is known to act as a global transcriptional regulator, miRNAs that are directly regulated by Mecp2 in the brain are not known. Using massively parallel sequencing methods, we have identified miRNAs whose expression is altered in cerebella of Mecp2-null mice before and after the onset of severe neurological symptoms. In vivo genome-wide analyses indicate that promoter regions of a significant fraction of dysregulated miRNA transcripts, including a large polycistronic cluster of brain-specific miRNAs, are DNA-methylated and are bound directly by Mecp2. Functional analysis demonstrates that the 3' UTR of messenger RNA encoding Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (Bdnf) can be targeted by multiple miRNAs aberrantly up-regulated in the absence of Mecp2. Taken together, these results suggest that dysregulation of miRNAs may contribute to RTT pathoetiology and also may provide a valuable resource for further investigations of the role of miRNAs in RTT.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Disrupted microRNA expression caused by Mecp2 loss in a mouse model of Rett syndrome.Epigenetics. 2010 Oct 1;5(7):656-63. doi: 10.4161/epi.5.7.13055. Epub 2010 Oct 1. Epigenetics. 2010. PMID: 20716963 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the possible link between MeCP2 and oxidative stress in Rett syndrome.Free Radic Biol Med. 2015 Nov;88(Pt A):81-90. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2015.04.019. Epub 2015 May 8. Free Radic Biol Med. 2015. PMID: 25960047 Review.
-
MeCP2-regulated miRNAs control early human neurogenesis through differential effects on ERK and AKT signaling.Mol Psychiatry. 2018 Apr;23(4):1051-1065. doi: 10.1038/mp.2017.86. Epub 2017 Apr 25. Mol Psychiatry. 2018. PMID: 28439102 Free PMC article.
-
Site-blocking antisense oligonucleotides as a mechanism to fine-tune MeCP2 expression.RNA. 2024 Nov 18;30(12):1554-1571. doi: 10.1261/rna.080220.124. RNA. 2024. PMID: 39379106 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation, diversity and function of MECP2 exon and 3'UTR isoforms.Hum Mol Genet. 2020 Sep 30;29(R1):R89-R99. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddaa154. Hum Mol Genet. 2020. PMID: 32681172 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Epigenome in Neurodevelopmental Disorders.Front Neurosci. 2021 Nov 3;15:776809. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.776809. eCollection 2021. Front Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34803599 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNAs downregulated in neuropathic pain regulate MeCP2 and BDNF related to pain sensitivity.FEBS Open Bio. 2015 Aug 31;5:733-40. doi: 10.1016/j.fob.2015.08.010. eCollection 2015. FEBS Open Bio. 2015. PMID: 26448907 Free PMC article.
-
A placental mammal-specific microRNA cluster acts as a natural brake for sociability in mice.EMBO Rep. 2019 Feb;20(2):e46429. doi: 10.15252/embr.201846429. Epub 2018 Dec 14. EMBO Rep. 2019. PMID: 30552145 Free PMC article.
-
DNA methylation directs microRNA biogenesis in mammalian cells.Nat Commun. 2019 Dec 11;10(1):5657. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-13527-1. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31827083 Free PMC article.
-
Mecp2 truncation in male mice promotes affiliative social behavior.Behav Genet. 2012 Mar;42(2):299-312. doi: 10.1007/s10519-011-9501-2. Epub 2011 Sep 11. Behav Genet. 2012. PMID: 21909962 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amir RE, et al. Rett syndrome is caused by mutations in X-linked MECP2, encoding methyl-CpG-binding protein 2. Nat Genet. 1999;23:185–188. - PubMed
-
- Chahrour M, Zoghbi HY. The story of Rett syndrome: From clinic to neurobiology. Neuron. 2007;56:422–437. - PubMed
-
- Chen RZ, Akbarian S, Tudor M, Jaenisch R. Deficiency of methyl-CpG binding protein-2 in CNS neurons results in a Rett-like phenotype in mice. Nat Genet. 2001;27:327–331. - PubMed
-
- Guy J, Hendrich B, Holmes M, Martin JE, Bird A. A mouse Mecp2-null mutation causes neurological symptoms that mimic Rett syndrome. Nat Genet. 2001;27:322–326. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

