Correction of respiratory disorders in a mouse model of Rett syndrome
- PMID: 20921395
- PMCID: PMC2964253
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1012104107
Correction of respiratory disorders in a mouse model of Rett syndrome
Abstract
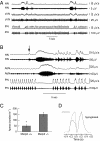
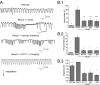
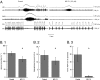
Rett syndrome (RTT) is an autism spectrum disorder caused by mutations in the X-linked gene that encodes the transcription factor methyl-CpG-binding protein 2 (MeCP2). A major debilitating phenotype in affected females is frequent apneas, and heterozygous Mecp2-deficient female mice mimic the human respiratory disorder. GABA defects have been demonstrated in the brainstem of Mecp2-deficient mice. Here, using an intact respiratory network, we show that apnea in RTT mice is characterized by excessive excitatory activity in expiratory cranial and spinal nerves. Augmenting GABA markedly improves the respiratory phenotype. In addition, a serotonin 1a receptor agonist that depresses expiratory neuron activity also reduces apnea, corrects the irregular breathing pattern, and prolongs survival in MeCP2 null males. Combining a GABA reuptake blocker with a serotonin 1a agonist in heterozygous females completely corrects their respiratory defects. The results indicate that GABA and serotonin 1a receptor activity are candidates for treatment of the respiratory disorders in Rett syndrome.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
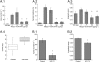
References
-
- Amir RE, et al. Rett syndrome is caused by mutations in X-linked MECP2, encoding methyl-CpG-binding protein 2. Nat Genet. 1999;23:185–188. - PubMed
-
- Bird A. The methyl-CpG-binding protein MeCP2 and neurological disease. Biochem Soc Trans. 2008;36:575–583. - PubMed
-
- Chahrour M, Zoghbi HY. The story of Rett syndrome: From clinic to neurobiology. Neuron. 2007;56:422–437. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

