Common variants in the ATP2B1 gene are associated with susceptibility to hypertension: the Japanese Millennium Genome Project
- PMID: 20921432
- PMCID: PMC5003412
- DOI: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.110.153429
Common variants in the ATP2B1 gene are associated with susceptibility to hypertension: the Japanese Millennium Genome Project
Abstract
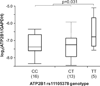
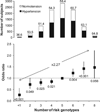
Hypertension is one of the most common complex genetic disorders. We have described previously 38 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) with suggestive association with hypertension in Japanese individuals. In this study we extend our previous findings by analyzing a large sample of Japanese individuals (n=14 105) for the most associated SNPs. We also conducted replication analyses in Japanese of susceptibility loci for hypertension identified recently from genome-wide association studies of European ancestries. Association analysis revealed significant association of the ATP2B1 rs2070759 polymorphism with hypertension (P=5.3×10(-5); allelic odds ratio: 1.17 [95% CI: 1.09 to 1.26]). Additional SNPs in ATP2B1 were subsequently genotyped, and the most significant association was with rs11105378 (odds ratio: 1.31 [95% CI: 1.21 to 1.42]; P=4.1×10(-11)). Association of rs11105378 with hypertension was cross-validated by replication analysis with the Global Blood Pressure Genetics consortium data set (odds ratio: 1.13 [95% CI: 1.05 to 1.21]; P=5.9×10(-4)). Mean adjusted systolic blood pressure was highly significantly associated with the same SNP in a meta-analysis with individuals of European descent (P=1.4×10(-18)). ATP2B1 mRNA expression levels in umbilical artery smooth muscle cells were found to be significantly different among rs11105378 genotypes. Seven SNPs discovered in published genome-wide association studies were also genotyped in the Japanese population. In the combined analysis with replicated 3 genes, FGF5 rs1458038, CYP17A1, rs1004467, and CSK rs1378942, odds ratio of the highest risk group was 2.27 (95% CI: 1.65 to 3.12; P=4.6×10(-7)) compared with the lower risk group. In summary, this study confirmed common genetic variation in ATP2B1, as well as FGF5, CYP17A1, and CSK, to be associated with blood pressure levels and risk of hypertension.
Figures
References
-
- Kotchen TA, Kotchen JM, Grim CE, George V, Kaldunski ML, Cowley AW, Hamet P, Chelius TH. Genetic determinants of hypertension: identification of candidate phenotypes. Hypertension. 2000;36:7–13. - PubMed
-
- Newton-Cheh C, Johnson T, Gateva V, Tobin MD, Bochud M, Coin L, Najjar SS, Zhao JH, Heath SC, Eyheramendy S, Papadakis K, Voight BF, Scott LJ, Zhang F, Farrall M, Tanaka T, Wallace C, Chambers JC, Khaw KT, Nilsson P, van der Harst P, Polidoro S, Grobbee DE, Onland-Moret NC, Bots ML, Wain LV, Elliott KS, Teumer A, Luan J, Lucas G, Kuusisto J, Burton PR, Hadley D, McArdle WL, for the Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium. Brown M, Dominiczak A, Newhouse SJ, Samani NJ, Webster J, Zeggini E, Beckmann JS, Bergmann S, Lim N, Song K, Vollenweider P, Waeber G, Waterworth DM, Yuan X, Groop L, Orho-Melander M, Allione A, Di Gregorio A, Guarrera S, Panico S, Ricceri F, Romanazzi V, Sacerdote C, Vineis P, Barroso I, Sandhu MS, Luben RN, Crawford GJ, Jousilahti P, Perola M, Boehnke M, Bonnycastle LL, Collins FS, Jackson AU, Mohlke KL, Stringham HM, Valle TT, Willer CJ, Bergman RN, Morken MA, Döring A, Gieger C, Illig T, Meitinger T, Org E, Pfeufer A, Wichmann HE, Kathiresan S, Marrugat J, O’Donnell CJ, Schwartz SM, Siscovick DS, Subirana I, Freimer NB, Hartikainen AL, McCarthy MI, O’Reilly PF, Peltonen L, Pouta A, de Jong PE, Snieder H, van Gilst WH, Clarke R, Goel A, Hamsten A, Peden JF, Seedorf U, Syvänen AC, Tognoni G, Lakatta EG, Sanna S, Scheet P, Schlessinger D, Scuteri A, Dörr M, Ernst F, Felix SB, Homuth G, Lorbeer R, Reffelmann T, Rettig R, Völker U, Galan P, Gut IG, Hercberg S, Lathrop GM, Zelenika D, Deloukas P, Soranzo N, Williams FM, Zhai G, Salomaa V, Laakso M, Elosua R, Forouhi NG, Völzke H, Uiterwaal CS, van der Schouw YT, Numans ME, Matullo G, Navis G, Berglund G, Bingham SA, Kooner JS, Connell JM, Bandinelli S, Ferrucci L, Watkins H, Spector TD, Tuomilehto J, Altshuler D, Strachan DP, Laan M, Meneton P, Wareham NJ, Uda M, Jarvelin MR, Mooser V, Melander O, Loos RJ, Elliott P, Abecasis GR, Caulfield M, Munroe PB. Genome-wide association study identifies eight loci associated with blood pressure. Nat Genet. 2009;41:666–676. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Levy D, Ehret GB, Rice K, Verwoert GC, Launer LJ, Dehghan A, Glazer NL, Morrison AC, Johnson AD, Aspelund T, Aulchenko Y, Lumley T, Köttgen A, Vasan RS, Rivadeneira F, Eiriksdottir G, Guo X, Arking DE, Mitchell GF, Mattace-Raso FU, Smith AV, Taylor K, Scharpf RB, Hwang SJ, Sijbrands EJ, Bis J, Harris TB, Ganesh SK, O’Donnell CJ, Hofman A, Rotter JI, Coresh J, Benjamin EJ, Uitterlinden AG, Heiss G, Fox CS, Witteman JC, Boerwinkle E, Wang TJ, Gudnason V, Larson MG, Chakravarti A, Psaty BM, van Duijn CM. Genome-wide association study of blood pressure and hypertension. Nat Genet. 2009;41:677–687. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cho YS, Go MJ, Kim YJ, Heo JY, Oh JH, Ban HJ, Yoon D, Lee MH, Kim DJ, Park M, Cha SH, Kim JW, Han BG, Min H, Ahn Y, Park MS, Han HR, Jang HY, Cho EY, Lee JE, Cho NH, Shin C, Park T, Park JW, Lee JK, Cardon L, Clarke G, McCarthy MI, Lee JY, Lee JK, Oh B, Kim HL. A large-scale genome-wide association study of Asian populations uncovers genetic factors influencing eight quantitative traits. Nat Genet. 2009;41:527–534. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

