Phase II selection design trial of concurrent chemotherapy and cetuximab versus chemotherapy followed by cetuximab in advanced-stage non-small-cell lung cancer: Southwest Oncology Group study S0342
- PMID: 20921467
- PMCID: PMC3020704
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2009.27.9356
Phase II selection design trial of concurrent chemotherapy and cetuximab versus chemotherapy followed by cetuximab in advanced-stage non-small-cell lung cancer: Southwest Oncology Group study S0342
Abstract
Purpose: Randomized clinical trials failed to show a survival benefit for epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitors plus concurrent chemotherapy in patients with metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC), with preclinical data suggesting potential negative interactions. In contrast, pilot trials of the EGFR-targeted antibody, cetuximab, plus chemotherapy suggested enhanced antitumor activity. This randomized phase II trial was designed to select a cetuximab plus chemotherapy regimen for phase III evaluation.
Patients and methods: Treatment-naive patients with advanced-stage NSCLC were randomly assigned to receive paclitaxel (225 mg/m(2)) and carboplatin (area under the curve, 6) every 3 weeks plus concurrent cetuximab (400 mg/m(2) loading dose followed by 250 mg/m(2) weekly) for four cycles followed by maintenance cetuximab or sequential paclitaxel-carboplatin for four cycles followed by cetuximab.
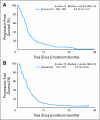
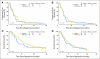
Results: Of 242 patients enrolled, 224 were eligible and assessable for response (106 and 118 patients in the concurrent and sequential arms, respectively). With a median follow-up time of 32 months, the median overall survival was 10.9 months (95% CI, 9.2 to 13.0 months) for patients receiving concurrent therapy and 10.7 months (95% CI, 8.5 to 12.8 months) for patients receiving sequential therapy (P = .57); 1-year survival rates were 45% (95% CI, 36% to 54%) and 44% (95% CI, 35% to 53%), respectively. Response rates and progression-free survival times were similar in both arms, as was grade 3 rash, whereas sensory neuropathy was higher in the concurrent arm (15% v 5% in the sequential arm; P = .036).
Conclusion: Although both regimens met the efficacy criterion for continued evaluation, the concurrent regimen of paclitaxel/carboplatin plus cetuximab was chosen.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Analysis of potential predictive markers of cetuximab benefit in BMS099, a phase III study of cetuximab and first-line taxane/carboplatin in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer.J Clin Oncol. 2010 Feb 20;28(6):918-27. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2009.25.2890. Epub 2010 Jan 25. J Clin Oncol. 2010. PMID: 20100958 Clinical Trial.
-
Cetuximab plus carboplatin and paclitaxel with or without bevacizumab versus carboplatin and paclitaxel with or without bevacizumab in advanced NSCLC (SWOG S0819): a randomised, phase 3 study.Lancet Oncol. 2018 Jan;19(1):101-114. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30694-0. Epub 2017 Nov 20. Lancet Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29169877 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Randomized phase II study of concurrent versus sequential alternating gefitinib and chemotherapy in previously untreated non-small cell lung cancer with sensitive EGFR mutations: NEJ005/TCOG0902.Ann Oncol. 2015 May;26(5):888-894. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdv063. Epub 2015 Feb 10. Ann Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25669832 Clinical Trial.
-
Personalized medicine in non-small-cell lung cancer: is KRAS a useful marker in selecting patients for epidermal growth factor receptor-targeted therapy?J Clin Oncol. 2010 Nov 1;28(31):4769-77. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2009.27.4365. Epub 2010 Oct 4. J Clin Oncol. 2010. PMID: 20921461 Review.
-
Inhibition of the epidermal growth factor receptor in combined modality treatment for locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer.Semin Oncol. 2005 Apr;32(2 Suppl 3):S35-41. doi: 10.1053/j.seminoncol.2005.03.008. Semin Oncol. 2005. PMID: 16015534 Review.
Cited by
-
A pediatric trial of radiation/cetuximab followed by irinotecan/cetuximab in newly diagnosed diffuse pontine gliomas and high-grade astrocytomas: A Pediatric Oncology Experimental Therapeutics Investigators' Consortium study.Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2017 Nov;64(11):10.1002/pbc.26621. doi: 10.1002/pbc.26621. Epub 2017 May 24. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28544128 Free PMC article.
-
Phase II trial of carboplatin, paclitaxel, cetuximab, and bevacizumab followed by cetuximab and bevacizumab in advanced nonsquamous non-small-cell lung cancer: SWOG S0536.J Thorac Oncol. 2013 Dec;8(12):1519-28. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0000000000000009. J Thorac Oncol. 2013. PMID: 24189513 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Optimizing the use of epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors in advanced non-small-lung cancer (NSCLC).J Thorac Dis. 2011 Mar;3(1):57-64. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2072-1439.2010.12.05. J Thorac Dis. 2011. PMID: 22263061 Free PMC article.
-
Avelumab in Combination With Cetuximab and Chemotherapy as First-Line Treatment for Patients With Advanced Squamous NSCLC.JTO Clin Res Rep. 2023 Jan 2;4(2):100461. doi: 10.1016/j.jtocrr.2022.100461. eCollection 2023 Feb. JTO Clin Res Rep. 2023. PMID: 36718142 Free PMC article.
-
Weekly and every 2 weeks cetuximab maintenance therapy after platinum-based chemotherapy plus cetuximab as first-line treatment for non-small cell lung cancer: randomized non-comparative phase IIIb NEXT trial.Target Oncol. 2015 Jun;10(2):255-65. doi: 10.1007/s11523-014-0336-7. Epub 2014 Sep 9. Target Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25195590 Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Kelly K, Crowley J, Bunn PA, Jr, et al. Randomized phase III trial of paclitaxel plus carboplatin versus vinorelbine plus cisplatin in the treatment of patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: A Southwest Oncology Group trial. J Clin Oncol. 2001;19:3210–3218. - PubMed
-
- Schiller JH, Harrington D, Belani CP, et al. Comparison of four chemotherapy regimens for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2002;346:92–98. - PubMed
-
- Sandler A, Gray R, Perry MC, et al. Paclitaxel-carboplatin alone or with bevacizumab for non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:2542–2550. - PubMed
-
- Giaccone G, Herbst RS, Manegold C, et al. Gefitinib in combination with gemcitabine and cisplatin in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: A phase III trial—INTACT 1. J Clin Oncol. 2004;22:777–784. - PubMed
-
- Herbst RS, Giaccone G, Schiller JH, et al. Gefitinib in combination with paclitaxel and carboplatin in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: A phase III trial—INTACT 2. J Clin Oncol. 2004;22:785–794. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- N01 CA004919/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA012644/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA22433/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA045808/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA68183/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA63850/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035178/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA76447/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA105409/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA76448/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA046368/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035090/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA063844/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA63848/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA37981/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA093373/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA022433/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA58416/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA027057/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA35128/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA037981/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA004919/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA035431/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA046113/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA045560/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA12644/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035128/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA20319/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA063850/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA076447/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA032102/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA014028/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA035119/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA45808/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180846/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA046441/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA063848/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA14028/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA58882/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA11083/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA58861/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA35090/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA46282/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA76132/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA063844/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA045450/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA032102/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA046282/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA45450/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA105409/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA035178/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA46368/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA67663/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA038926/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA067575/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA027057/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA046441/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA233340/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA058882/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA020319/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA46113/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA038926/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA042777/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035431/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035119/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA42777/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA011083/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA067575/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA067663/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA058861/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA068183/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA045560/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

