Distinct growth hormone receptor signaling modes regulate skeletal muscle development and insulin sensitivity in mice
- PMID: 20921627
- PMCID: PMC2964973
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI42447
Distinct growth hormone receptor signaling modes regulate skeletal muscle development and insulin sensitivity in mice
Abstract
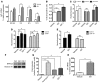
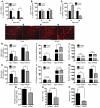
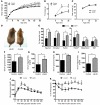
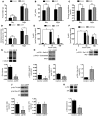
Skeletal muscle development, nutrient uptake, and nutrient utilization is largely coordinated by growth hormone (GH) and its downstream effectors, in particular, IGF-1. However, it is not clear which effects of GH on skeletal muscle are direct and which are secondary to GH-induced IGF-1 expression. Thus, we generated mice lacking either GH receptor (GHR) or IGF-1 receptor (IGF-1R) specifically in skeletal muscle. Both exhibited impaired skeletal muscle development characterized by reductions in myofiber number and area as well as accompanying deficiencies in functional performance. Defective skeletal muscle development, in both GHR and IGF-1R mutants, was attributable to diminished myoblast fusion and associated with compromised nuclear factor of activated T cells import and activity. Strikingly, mice lacking GHR developed metabolic features that were not observed in the IGF-1R mutants, including marked peripheral adiposity, insulin resistance, and glucose intolerance. Insulin resistance in GHR-deficient myotubes derived from reduced IR protein abundance and increased inhibitory phosphorylation of IRS-1 on Ser 1101. These results identify distinct signaling pathways through which GHR regulates skeletal muscle development and modulates nutrient metabolism.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Deletion of growth hormone receptors in postnatal skeletal muscle of male mice does not alter muscle mass and response to pathological injury.Endocrinology. 2013 Oct;154(10):3776-83. doi: 10.1210/en.2013-1209. Epub 2013 Jul 16. Endocrinology. 2013. PMID: 23861377 Free PMC article.
-
Growth hormone promotes skeletal muscle cell fusion independent of insulin-like growth factor 1 up-regulation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 May 9;103(19):7315-20. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0510033103. Epub 2006 May 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16670201 Free PMC article.
-
Growth hormone receptor gene deficiency causes delayed insulin responsiveness in skeletal muscles without affecting compensatory islet cell overgrowth in obese mice.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2006 Sep;291(3):E491-8. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00378.2005. Epub 2006 Apr 18. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2006. PMID: 16621895
-
Growth hormone and the insulin-like growth factor system in myogenesis.Endocr Rev. 1996 Oct;17(5):481-517. doi: 10.1210/edrv-17-5-481. Endocr Rev. 1996. PMID: 8897022 Review.
-
Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) and aging: controversies and new insights.Biogerontology. 2003;4(1):1-8. doi: 10.1023/a:1022448532248. Biogerontology. 2003. PMID: 12652183 Review.
Cited by
-
Tissue-Specific GHR Knockout Mice: Metabolic Phenotypes.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2015 Jan 19;5:243. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2014.00243. eCollection 2014. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2015. PMID: 25646092 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Growth Hormone and Craniofacial Tissues. An update.Open Dent J. 2015 Jan 30;9:1-8. doi: 10.2174/1874210601509010001. eCollection 2015. Open Dent J. 2015. PMID: 25674165 Free PMC article.
-
Dexamethasone and BCAA Failed to Modulate Muscle Mass and mTOR Signaling in GH-Deficient Rats.PLoS One. 2015 Jun 18;10(6):e0128805. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0128805. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26086773 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of growth hormone on insulin signaling.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2020 Dec 1;518:111038. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2020.111038. Epub 2020 Sep 20. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2020. PMID: 32966863 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA-100 Reduced Fetal Bovine Muscle Satellite Cell Myogenesis and Augmented Intramuscular Lipid Deposition by Modulating IGF1R.Cells. 2022 Jan 28;11(3):451. doi: 10.3390/cells11030451. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35159261 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

