Mesothelin as a potential therapeutic target in human cholangiocarcinoma
- PMID: 20922056
- PMCID: PMC2948219
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.1.141
Mesothelin as a potential therapeutic target in human cholangiocarcinoma
Abstract
Background: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and cholangiocarcinoma (CCA) are the two most common primary liver cancers, yet there have been no significant advances in effective therapeutics. Mesothelin has been reported as a new therapeutic target in various types of cancer. Here, we investigated the expression of mesothelin in liver cancer and its potential role as a novel therapeutic target for immunotherapy.
Methods: HCC and CCA specimens were examined by immunohistochemistry for mesothelin expression. Protein expression was assessed by immunoblotting and flow cytometry. The SS1P immunotoxin targeting mesothelin was evaluated in the well-established CCA cell lines HuCCT1, HuH-28, KMBC, KMCH, Mz-ChA-1 and OZ.
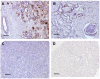
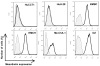
Results: We showed strong immunochemical mesothelin staining in 33% of the surgically resected CCA specimens and 3 of 6 CCA cell lines (OZ, KMBC and KMCH). No mesothelin staining was found in HCC or normal liver tissue. Mesothelin was primarily localized to the cellular plasma membrane and the mature form (molecular weight, ~40 kDa) was expressed at a high level in CCA tissues. Moreover, 22% of CCA specimens had a high mesothelin expression level which was comparable to the CCA cell line models. Interestingly, SS1P showed very high and specific growth inhibition when added to mesothelin-expressing CCA cells with IC(50) values ranging from 0.5 to 11 ng/mL.
Conclusions: Mesothelin is overexpressed in one-third of CCA tissues. SS1P targeting mesothelin reveals a remarkable single agent activity against CCA in vitro. These findings indicate a potential for SS1P in the immunotherapeutic treatment of CCA.
Keywords: SS1P; bile duct carcinoma; cholangiocarcinoma; hepatocellular carcinoma; immunotoxin; mesothelin.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: The authors have declared that no conflict of interest exists.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Mesothelin expression in human lung cancer.Clin Cancer Res. 2007 Mar 1;13(5):1571-5. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-2161. Clin Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17332303
-
Differential Expression of Sonic Hedgehog Protein in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma.Pathol Oncol Res. 2015 Sep;21(4):901-8. doi: 10.1007/s12253-015-9918-7. Epub 2015 Mar 5. Pathol Oncol Res. 2015. PMID: 25740074
-
Prostate-specific membrane antigen expression in hepatocellular carcinoma, cholangiocarcinoma, and liver cirrhosis.World J Gastroenterol. 2020 Dec 28;26(48):7664-7678. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i48.7664. World J Gastroenterol. 2020. PMID: 33505143 Free PMC article.
-
Mesothelin Expression in Advanced Gastroesophageal Cancer Represents a Novel Target for Immunotherapy.Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 2016 Apr;24(4):246-52. doi: 10.1097/PAI.0000000000000292. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 2016. PMID: 26894650 Free PMC article.
-
Mesothelin: a new target for immunotherapy.Clin Cancer Res. 2004 Jun 15;10(12 Pt 1):3937-42. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-03-0801. Clin Cancer Res. 2004. PMID: 15217923 Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of Mesothelin in Activation of Portal Fibroblasts in Cholestatic Liver Injury.Biology (Basel). 2022 Oct 28;11(11):1589. doi: 10.3390/biology11111589. Biology (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36358290 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Engineered Fn3 protein has targeted therapeutic effect on mesothelin-expressing cancer cells and increases tumor cell sensitivity to chemotherapy.Biotechnol Bioeng. 2020 Feb;117(2):330-341. doi: 10.1002/bit.27204. Epub 2019 Nov 12. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2020. PMID: 31631324 Free PMC article.
-
A network-biology approach for identification of key genes and pathways involved in malignant peritoneal mesothelioma.Genomics Inform. 2021 Jun;19(2):e16. doi: 10.5808/gi.21019. Epub 2021 Jun 30. Genomics Inform. 2021. PMID: 34261301 Free PMC article.
-
Immune-Mediated Therapies for Liver Cancer.Genes (Basel). 2017 Feb 17;8(2):76. doi: 10.3390/genes8020076. Genes (Basel). 2017. PMID: 28218682 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel Humanized Mesothelin-Expressing Genetically Engineered Mouse Models Underscore Challenges in Delivery of Complex Therapeutics to Pancreatic Cancers.Mol Cancer Ther. 2021 Oct;20(10):2082-2092. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-21-0017. Epub 2021 Jul 26. Mol Cancer Ther. 2021. PMID: 34315768 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Spangenberg HC, Thimme R, Blum HE. Targeted therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009;6:423–32. - PubMed
-
- Patel T. Increasing incidence and mortality of primary intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma in the United States. Hepatology. 2001;33:1353–7. - PubMed
-
- Shaib Y, El-Serag HB. The epidemiology of cholangiocarcinoma. Semin Liver Dis. 2004;24:115–25. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

