Measurement of HbA1c from stored whole blood samples in the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities study
- PMID: 20923494
- PMCID: PMC2991637
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1753-0407.2010.00070.x
Measurement of HbA1c from stored whole blood samples in the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities study
Abstract
Background: The aims of the present study were to demonstrate the reliability of HbA1c measurements during two time periods and to compare these measurements with HbA1c distribution in the general US population.
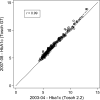
Methods: HbA1c was measured in 14,069 whole blood samples in the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) study using different HPLC instruments across two time periods, namely 2003-2004 and 2007-2008. At the time of measurement, samples had been in storage at -70°C for up to 18 years. To assess differences in values, HbA1c measurements were repeated in 383 samples at both periods. Indirect comparisons were made by comparing our measurements against those from a nationally representative study.
Results: The coefficients of variation for quality control samples were 1.8% (n = 89) in 2003-2004 and 1.4% (n = 259) in 2007-2008. The correlation between measurements at the two time points was high (r = 0.99), but with a slight bias: 0.29% points higher in 2007-2008 vs 2003-2004 (n = 383; P < 0.0001). The comparison yielded the following Deming regression equation: y((2007-2008)) = 0.073 + 1.034x((2003-2004)) . After alignment using this equation, the distribution of HbA1c in the ARIC study was similar to that in the national study using fresh samples.
Conclusions: Measurements of HbA1c from samples stored for up to 18 years are highly reliable when using state-of-the-art HPLC instruments, but with some bias introduced over time. The HbA1c data now available in the ARIC study should be invaluable for investigations into the clinical utility of HbA1c as a diagnostic test for diabetes.
© 2010 Ruijin Hospital, Shanghai Jiaotong University School of Medicine and Blackwell Publishing Asia Pty Ltd.
Figures



References
-
- Survey Operations Manuals, Brochures, and Consent Documents: 1999–current NHANES. National Center for Health Statistics, Centers for Disease Control; 2007. http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/about/major/nhanes/currentnhanes.htm (accessed xxx)
-
- NHANES III Data Files, Documentation, and Codebooks. 2006. (Accessed at.
-
- Steffes M, Cleary P, Goldstein D, et al. Hemoglobin A1c measurements over nearly two decades: Sustaining comparable values throughout the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial and the Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications Study. Clinical Chemistry. 2005;51:753–8. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- N01 HC055016/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC055019/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-55016/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC055015/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-55021/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-55019/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-55015/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-55020/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC055018/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC055022/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 DK080294/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-55018/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-55022/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC055021/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC055020/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K01 DK076595/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

