Regulation of Hip1r by epsin controls the temporal and spatial coupling of actin filaments to clathrin-coated pits
- PMID: 20923836
- PMCID: PMC2964106
- DOI: 10.1242/jcs.066852
Regulation of Hip1r by epsin controls the temporal and spatial coupling of actin filaments to clathrin-coated pits
Abstract
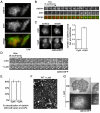
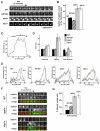
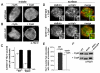
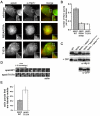
Recently, it has become clear that the actin cytoskeleton is involved in clathrin-mediated endocytosis. During clathrin-mediated endocytosis, clathrin triskelions and adaptor proteins assemble into lattices, forming clathrin-coated pits. These coated pits invaginate and detach from the membrane, a process that requires dynamic actin polymerization. We found an unexpected role for the clathrin adaptor epsin in regulating actin dynamics during this late stage of coated vesicle formation. In Dictyostelium cells, epsin is required for both the membrane recruitment and phosphorylation of the actin- and clathrin-binding protein Hip1r. Epsin-null and Hip1r-null cells exhibit deficiencies in the timing and organization of actin filaments at clathrin-coated pits. Consequently, clathrin structures persist on the membranes of epsin and Hip1r mutants and the internalization of clathrin structures is delayed. We conclude that epsin works with Hip1r to regulate actin dynamics by controlling the spatial and temporal coupling of actin filaments to clathrin-coated pits. Specific residues in the ENTH domain of epsin that are required for the membrane recruitment and phosphorylation of Hip1r are also required for normal actin and clathrin dynamics at the plasma membrane. We propose that epsin promotes the membrane recruitment and phosphorylation of Hip1r, which in turn regulates actin polymerization at clathrin-coated pits.
Figures
References
-
- Aguilar R. C., Watson H. A., Wendland B. (2003). The yeast Epsin Ent1 is recruited to membranes through multiple independent interactions. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 10737-10743 - PubMed
-
- Aguilar R. C., Longhi S. A., Shaw J. D., Yeh L. Y., Kim S., Schon A., Freire E., Hsu A., McCormick W. K., Watson H. A., et al. (2006). Epsin N-terminal homology domains perform an essential function regulating Cdc42 through binding Cdc42 GTPase-activating proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 103, 4116-4121 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brady R. J., Wen Y., O'Halloran T. J. (2008). The ENTH and C-terminal domains of Dictyostelium epsin cooperate to regulate the dynamic interaction with clathrin-coated pits. J. Cell Sci. 121, 3433-3444 - PubMed
-
- Bretschneider T., Diez S., Anderson K., Heuser J., Clarke M., Muller-Taubenberger A., Kohler J., Gerisch G. (2004). Dynamic actin patterns and Arp2/3 assembly at the substrate-attached surface of motile cells. Curr. Biol. 14, 1-10 - PubMed
-
- Chen C. Y., Brodsky F. M. (2005). Huntingtin-interacting protein 1 (Hip1) and Hip1-related protein (Hip1R) bind the conserved sequence of clathrin light chains and thereby influence clathrin assembly in vitro and actin distribution in vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 6109-6117 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

