Bulk segregation mapping of mutations in closely related strains of mice
- PMID: 20923982
- PMCID: PMC2998299
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.110.121160
Bulk segregation mapping of mutations in closely related strains of mice
Abstract
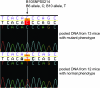
Phenovariance may be obscured when genetic mapping is performed using highly divergent strains, and closely similar strains are preferred if adequate marker density can be established. We sequenced the C57BL/10J mouse genome using the Applied Biosystems SOLiD platform and here describe a genome-wide panel of informative markers that permits the mapping of mutations induced on the closely related C57BL/6J background by outcrossing to C57BL/10J, and backcrossing or intercrossing. The panel consists of 127 single nucleotide polymorphisms validated by capillary sequencing: 124 spaced at ∼20-Mb intervals across the 19 autosomes, and three markers on the X chromosome. We determined the genetic relationship between four C57BL-derived substrains and used the panel to map two N-ethyl-N-nitrosourea (ENU)-induced mutations responsible for visible phenotypes in C57BL/6J mice through bulk segregation analysis. Capillary sequencing, with computation of relative chromatogram peak heights, was used to determine the proportion of alleles from each strain at each marker.
Figures



References
-
- Avraham, K. B., T. Hasson, K. P. Steel, D. M. Kingsley, L. B. Russell et al., 1995. The mouse Snell's waltzer deafness gene encodes an unconventional myosin required for structural integrity of inner ear hair cells. Nat. Genet. 11 369–375. - PubMed
-
- Collin, G. B., Y. Asada, D. S. Varnum and J. H. Nadeau, 1996. DNA pooling as a quick method for finding candidate linkages in multigenic trait analysis: An example involving susceptibility to germ cell tumors. Mamm. Genome 7 68–70. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

