Redox regulation of the stability of the SUMO protease SENP3 via interactions with CHIP and Hsp90
- PMID: 20924358
- PMCID: PMC2989103
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2010.245
Redox regulation of the stability of the SUMO protease SENP3 via interactions with CHIP and Hsp90
Abstract
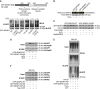
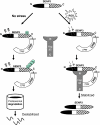
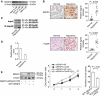
The molecular chaperone heat shock protein 90 (Hsp90) and the co-chaperone/ubiquitin ligase carboxyl terminus of Hsc70-interacting protein (CHIP) control the turnover of client proteins. How this system decides to stabilize or degrade the client proteins under particular physiological or pathological conditions is unclear. We report here a novel client protein, the SUMO2/3 protease SENP3, that is sophisticatedly regulated by CHIP and Hsp90. SENP3 is maintained at a low basal level under non-stress condition due to Hsp90-independent CHIP-mediated ubiquitination. Upon mild oxidative stress, SENP3 undergoes thiol modification, which recruits Hsp90. Hsp90/SENP3 association protects SENP3 from CHIP-mediated ubiquitination and subsequent degradation, but this effect of Hsp90 requires the presence of CHIP. Our data demonstrate for the first time that CHIP and Hsp90 interplay with a client alternately under non-stress and stress conditions, and the choice between stabilization and degradation is made by the redox state of the client. In addition, enhanced SENP3/Hsp90 association is found in cancer. These findings provide new mechanistic insight into how cells regulate the SUMO protease in response to oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Broadley SA, Hartl FU (2009) The role of molecular chaperones in human misfolding diseases. FEBS Lett 583: 2647–2653 - PubMed
-
- Chiosis G, Vilenchik M, Kim J, Solit D (2004) Hsp90: the vulnerable chaperone. Drug Discov Today 9: 881–888 - PubMed
-
- Cyr DM, Hohfeld J, Patterson C (2002) Protein quality control: U-box-containing E3 ubiquitin ligases join the fold. Trends Biochem Sci 27: 368–375 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

