Bishydrazide glycoconjugates for lectin recognition and capture of bacterial pathogens
- PMID: 20925370
- PMCID: PMC2987539
- DOI: 10.1021/bc100288c
Bishydrazide glycoconjugates for lectin recognition and capture of bacterial pathogens
Abstract
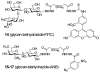
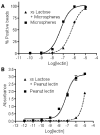
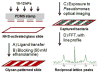
Bishydrazides are versatile linkers for attaching glycans to substrates for lectin binding and pathogen detection schemes. The α,ω-bishydrazides of carboxymethylated hexa(ethylene glycol) (4) can be conjugated at one end to unprotected oligosaccharides, then attached onto carrier proteins, tethered onto activated carboxyl-terminated surfaces, or functionalized with a photoactive cross-linking agent for lithographic patterning. Glycoconjugates of bishydrazide 4 can also be converted into dithiocarbamates (DTCs) by treatment with CS(2) under mild conditions, for attachment onto gold substrates. The immobilized glycans serve as recognition elements for cell-surface lectins and enable the detection and capture of bacterial pathogens such as Pseudomonas aeruginosa by their adsorption onto micropatterned substrates. A detection limit of 10³ cfu/mL is demonstrated, using a recently introduced method based on optical pattern recognition.
Figures




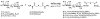

References
-
- Wang HF, Gu LR, Lin Y, Lu FS, Meziani MJ, Luo PGJ, Wang W, Cao L, Sun YP. Unique aggregation of anthrax (Bacillus anthracis) spores by sugarcoated single-walled carbon nanotubes. J Am Chem Soc. 2006;128:13364–13365. - PubMed
-
- El-Boubbou K, Gruden C, Huang X. Magnetic glyco-nanoparticles: A unique tool for rapid pathogen detection, decontamination, and strain differentiation. J Am Chem Soc. 2007;129:13392–13393. - PubMed
-
- Kale RR, Mukundan H, Price DN, Harris JF, Lewallen DM, Swanson BI, Schmidt GJ, Iyer SS. Detection of intact influenza viruses using biotinylated biantennary S-sialosides. J Am Chem Soc. 2008;130:8169–8171. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

