Comparison of real-time PCR and microscopy for malaria parasite detection in Malawian pregnant women
- PMID: 20925928
- PMCID: PMC2984567
- DOI: 10.1186/1475-2875-9-269
Comparison of real-time PCR and microscopy for malaria parasite detection in Malawian pregnant women
Abstract
Background: New diagnostic tools for malaria are required owing to the changing epidemiology of malaria, particularly among pregnant women in sub-Saharan Africa. Real-time PCR assays targeting Plasmodium falciparum lactate dehydrogenase (pfldh) gene may facilitate the identification of a high proportion of pregnant women with a P. falciparum parasitaemia below the threshold of microscopy. These molecular methods will enable further studies on the effects of these submicroscopic infections on maternal health and birth outcomes.
Methods: The pfldh real-time PCR assay and conventional microscopy were compared for the detection of P. falciparum from dried blood spots and blood smears collected from the peripheral blood of 475 Malawian women at delivery. A cycle threshold (Ct) of the real-time PCR was determined optimizing the sensitivity and specificity of the pfldh PCR assay compared to microscopy. A real-time PCR species-specific assay was applied to identify the contribution to malaria infections of three Plasmodium species (P. falciparum P. ovale and P. malariae) in 44 discordant smear and pfldh PCR assay results.
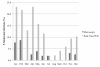
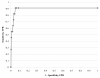
Results: Of the 475 women, P. falciparum was detected in 11 (2.3%) by microscopy and in 51 (10.7%) by real-time PCR; compared to microscopy, the sensitivity of real-time PCR was 90.9% and the specificity 91.2%. If a Ct value of 38 was used as a cut-off, specificity improved to 94.6% with no change in sensitivity. The real-time PCR species-specific assay detected P. falciparum alone in all but four samples: two samples were mixed infections with P. falciparum and P. malariae, one was a pure P. malariae infection and one was a pfldh PCR assay-positive/species-specific assay-negative sample. Of three P. malariae infections detected by microscopy, only one was confirmed by the species-specific assay.
Conclusions: Although microscopy remains the most appropriate method for clinical malaria diagnosis in field settings, molecular diagnostics such as real-time PCR offer a more reliable means to detect malaria parasites, particularly at low levels. Determination of the possible contribution of these submicroscopic infections to poor birth outcomes and maternal health is critical. For future studies to investigate these effects, this pfldh real-time PCR assay offers a reliable detection method.
Figures
References
-
- Steketee RW, Nahlen BL, Parise ME, Menendez C. The burden of malaria in pregnancy in malaria-endemic areas. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2001;64(Suppl 1-2):28–35. - PubMed
-
- Verhoeff FH, Brabin BJ, Chimsuku L, Kazembe P, Russell WB, Broadhead RL. An evaluation of the effects of intermittent sulfadoxine-pyrimethamine treatment in pregnancy on parasite clearance and risk of low birthweight in rural Malawi. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1998;92:141–150. doi: 10.1080/00034989859979. - DOI - PubMed
-
- van Eijk AM, Ayisi JG, ter Kuile FO, Otieno JA, Misore AO, Odondi JO, Rosen DH, Kager PA, Steketee RW, Nahlen BL. Effectiveness of intermittent preventive treatment with sulphadoxine-pyrimethamine for control of malaria in pregnancy in western Kenya: a hospital-based study. Trop Med Int Health. 2004;9:351–360. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3156.2004.01196.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Garner P, Gülmezoglu AM. Drugs for preventing malaria in pregnant women. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2006;18:CD000169. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical