Serotonin, but not N-methyltryptamines, activates the serotonin 2A receptor via a ß-arrestin2/Src/Akt signaling complex in vivo
- PMID: 20926677
- PMCID: PMC3001293
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1665-10.2010
Serotonin, but not N-methyltryptamines, activates the serotonin 2A receptor via a ß-arrestin2/Src/Akt signaling complex in vivo
Abstract
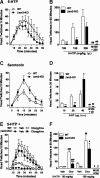
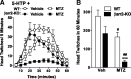
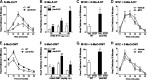
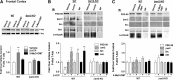
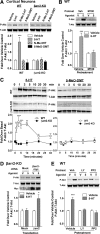
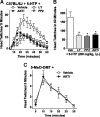
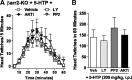
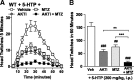
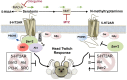
Hallucinogens mediate many of their psychoactive effects by activating serotonin 2A receptors (5-HT(2A)R). Although serotonin is the cognate endogenous neurotransmitter and is not considered hallucinogenic, metabolites of serotonin also have high affinity at 5-HT(2A)R and can induce hallucinations in humans. Here we report that serotonin differs from the psychoactive N-methyltryptamines by its ability to engage a β-arrestin2-mediated signaling cascade in the frontal cortex. Serotonin and 5-hydroxy-L-tryptophan (5-HTP) induce a head-twitch response in wild-type (WT) mice that is a behavioral proxy for 5-HT(2A)R activation. The response in β-arrestin2 knock-out (βarr2-KO) mice is greatly attenuated until the doses are elevated, at which point, βarr2-KO mice display a head-twitch response that can exceed that of WT mice. Direct administration of N-methyltryptamines also produces a greater response in βarr2-KO mice. Moreover, the inhibition of N-methyltransferase blocks 5-HTP-induced head twitches in βarr2-KO mice, indicating that N-methyltryptamines, rather than serotonin, primarily mediate this response. Biochemical studies demonstrate that serotonin stimulates Akt phosphorylation in the frontal cortex and in primary cortical neurons through the activation of a β-arrestin2/phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Src/Akt cascade, whereas N-methyltryptamines do not. Furthermore, disruption of any of the components of this cascade prevents 5-HTP-induced, but not N-methyltryptamine-induced, head twitches. We propose that there is a bifurcation of 5-HT(2A)R signaling that is neurotransmitter and β-arrestin2 dependent. This demonstration of agonist-directed 5-HT(2A)R signaling in vivo may significantly impact drug discovery efforts for the treatment of disorders wherein hallucinations are part of the etiology, such as schizophrenia, or manifest as side effects of treatment, such as depression.
Figures
References
-
- Aghajanian GK, Marek GJ. Serotonin and hallucinogens. Neuropsychopharmacology. 1999;21:16S–23S. - PubMed
-
- Angrist B, Thompson H, Shopsin B, Gershon S. Clinical studies with dopamine-receptor stimulants. Psychopharmacologia. 1975;44:273–280. - PubMed
-
- Arnt J, Hyttel J. Facilitation of 8-OHDPAT-induced forepaw treading of rats by the 5-HT2 agonist DOI. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989;161:45–51. - PubMed
-
- Askwith CC, Wemmie JA, Price MP, Rokhlina T, Welsh MJ. Acid-sensing ion channel 2 (ASIC2) modulates ASIC1 H+-activated currents in hippocampal neurons. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:18296–18305. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
