Isolation of a novel Orientia species (O. chuto sp. nov.) from a patient infected in Dubai
- PMID: 20926708
- PMCID: PMC3008486
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.01526-10
Isolation of a novel Orientia species (O. chuto sp. nov.) from a patient infected in Dubai
Abstract
In July 2006, an Australian tourist returning from Dubai, in the United Arab Emirates (UAE), developed acute scrub typhus. Her signs and symptoms included fever, myalgia, headache, rash, and eschar. Orientia tsutsugamushi serology demonstrated a 4-fold rise in antibody titers in paired serum collections (1:512 to 1:8,192), with the sera reacting strongest against the Gilliam strain antigen. An Orientia species was isolated by the in vitro culture of the patient's acute blood taken prior to antibiotic treatment. The gene sequencing of the 16S rRNA gene (rrs), partial 56-kDa gene, and the full open reading frame 47-kDa gene was performed, and comparisons of this new Orientia sp. isolate to previously characterized strains demonstrated significant sequence diversity. The closest homology to the rrs sequence of the new Orientia sp. isolate was with three strains of O. tsutsugamushi (Ikeda, Kato, and Karp), with a nucleotide sequence similarity of 98.5%. The closest homology to the 47-kDa gene sequence was with O. tsutsugamushi strain Gilliam, with a nucleotide similarity of 82.3%, while the closest homology to the 56-kDa gene sequence was with O. tsutsugamushi strain TA686, with a nucleotide similarity of 53.1%. The molecular divergence and geographically unique origin lead us to believe that this organism should be considered a novel species. Therefore, we have proposed the name "Orientia chuto," and the prototype strain of this species is strain Dubai, named after the location in which the patient was infected.
Figures


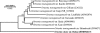



References
-
- Currie, B., D. Lo, P. Marks, G. Lum, P. Whelan, and V. Krause. 1996. Fatal scrub typhus from Litchfield Park, Northern Territory. Clin. Infect. Dis. 20:420-421.
-
- Enatsu, T., H. Urakami, and A. Tamura. 1999. Phylogenetic analysis of Orientia tsutsugamushi strains based on the sequence homologies of 56-kDa type-specific antigen genes. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 180:163-169. - PubMed
-
- Graves, S., B. Dwyer, D. McColl, and J. McDade. 1991. Flinders Island spotted fever: a newly recognised endemic focus of tick typhus in Bass Strait. Part 2: serological investigations. Med. J. Australia 154:99-103. - PubMed
-
- Graves, S., L. Wang, Z. Nack, and S. Jones. 1999. Rickettsia serosurvey in Kimberley, Western Australia. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 60:786-789. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

