Inhibition of cell adhesion by anti-P-selectin aptamer: a new potential therapeutic agent for sickle cell disease
- PMID: 20926770
- PMCID: PMC3031491
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2010-05-285718
Inhibition of cell adhesion by anti-P-selectin aptamer: a new potential therapeutic agent for sickle cell disease
Abstract
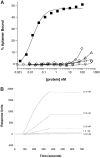
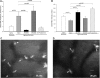
Adhesive interactions between circulating sickle red blood cells (RBCs), leukocytes, and endothelial cells are major pathophysiologic events in sickle cell disease (SCD). To develop new therapeutics that efficiently inhibit adhesive interactions, we generated an anti-P-selectin aptamer and examined its effects on cell adhesion using knockout-transgenic SCD model mice. Aptamers, single-stranded oligonucleotides that bind molecular targets with high affinity and specificity, are emerging as new therapeutics for cardiovascular and hematologic disorders. In vitro studies found that the anti-P-selectin aptamer exhibits high specificity to mouse P-selectin but not other selectins. SCD mice were injected with the anti-P-selectin aptamer, and cell adhesion was observed under hypoxia. The anti-P-selectin aptamer inhibited the adhesion of sickle RBCs and leukocytes to endothelial cells by 90% and 80%, respectively. The anti-P-selectin aptamer also increased microvascular flow velocities and reduced the leukocyte rolling flux. SCD mice treated with the anti-P-selectin aptamer demonstrated a reduced mortality rate associated with the experimental procedures compared with control mice. These results demonstrate that anti-P-selectin aptamer efficiently inhibits the adhesion of both sickle RBCs and leukocytes to endothelial cells in SCD model mice, suggesting a critical role for P-selectin in cell adhesion. Anti-P-selectin aptamer may be useful as a novel therapeutic agent for SCD.
Figures




Comment in
-
Aptamer therapy for SCD?Blood. 2011 Jan 13;117(2):379-80. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-11-313858. Blood. 2011. PMID: 21233323 No abstract available.
References
-
- Hebbel RP, Boogaerts MA, Eaton JW, Steinberg MH. Erythrocyte adherence to endothelium in sickle-cell anemia. A possible determinant of disease severity. N Engl J Med. 1980;302(18):992–995. - PubMed
-
- Pan J, Xia L, McEver RP. Comparison of promoters for the murine and human P-selectin genes suggests species-specific and conserved mechanisms for transcriptional regulation in endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1998;273(16):10058–10067. - PubMed
-
- Matsui NM, Borsig L, Rosen SD, Yaghmai M, Varki A, Embury SH. P-selectin mediates the adhesion of sickle erythrocytes to the endothelium. Blood. 2001;98(6):1955–1962. - PubMed
-
- Eppihimer MJ, Wolitzky B, Anderson DC, Labow MA, Granger DN. Heterogeneity of expression of E- and P-selectins in vivo. Circ Res. 1996;79(3):560–569. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

