Therapeutic targeting of C-terminal binding protein in human cancer
- PMID: 20930544
- PMCID: PMC3047800
- DOI: 10.4161/cc.9.18.12936
Therapeutic targeting of C-terminal binding protein in human cancer
Abstract
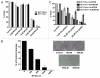
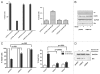
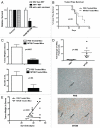
The CtBP transcriptional corepressors promote cancer cell survival and migration/invasion. CtBP senses cellular metabolism via a regulatory dehydrogenase domain, and is antagonized by p14/p19(ARF) tumor suppressors. The CtBP dehydrogenase substrate 4-methylthio-2-oxobutyric acid (MTOB) can act as a CtBP inhibitor at high concentrations, and is cytotoxic to cancer cells. MTOB induced apoptosis was p53-independent, correlated with the derepression of the proapoptotic CtBP repression target Bik, and was rescued by CtBP overexpression or Bik silencing. MTOB did not induce apoptosis in mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs), but was increasingly cytotoxic to immortalized and transformed MEFs, suggesting that CtBP inhibition may provide a suitable therapeutic index for cancer therapy. In human colon cancer cell peritoneal xenografts, MTOB treatment decreased tumor burden and induced tumor cell apoptosis. To verify the potential utility of CtBP as a therapeutic target in human cancer, the expression of CtBP and its negative regulator ARF was studied in a series of resected human colon adenocarcinomas. CtBP and ARF levels were inversely-correlated, with elevated CtBP levels (compared with adjacent normal tissue) observed in greater than 60% of specimens, with ARF absent in nearly all specimens exhibiting elevated CtBP levels. Targeting CtBP may represent a useful therapeutic strategy in human malignancies.
Figures


Comment in
-
Incapacitating CtBP to kill cancer.Cell Cycle. 2010 Sep 15;9(18):3645-6. doi: 10.4161/cc.9.18.13221. Epub 2010 Sep 15. Cell Cycle. 2010. PMID: 20930508 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Subramanian T, Chinnadurai G. Association of class I histone deacetylases with transcriptional corepressor CtBP. FEBS Lett. 2003;540:255–258. - PubMed
-
- Chinnadurai G. CtBP family proteins: more than transcriptional corepressors. Bioessays. 2003;25:9–12. - PubMed
-
- Boyd JM, Subramanian T, Schaeper U, La Regina M, Bayley S, Chinnadurai G. A region in the C-terminus of adenovirus 2/5 E1a protein is required for association with a cellular phosphoprotein and important for the negative modulation of T24-ras mediated transformation, tumorigenesis and metastasis. EMBO J. 1993;12:469–478. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Schaeper U, Boyd JM, Verma S, Uhlmann E, Subramanian T, Chinnadurai G. Molecular cloning and characterization of a cellular phosphoprotein that interacts with a conserved C-terminal domain of adenovirus E1A involved in negative modulation of oncogenic transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1995;92:10467–10471. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bergman LM, Blaydes JP. C-terminal binding proteins: emerging roles in cell survival and tumorigenesis. Apoptosis. 2006;11:879–888. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
