Mechanistic understanding of Pyrococcus horikoshii Dph2, a [4Fe-4S] enzyme required for diphthamide biosynthesis
- PMID: 20931132
- PMCID: PMC3066188
- DOI: 10.1039/c0mb00076k
Mechanistic understanding of Pyrococcus horikoshii Dph2, a [4Fe-4S] enzyme required for diphthamide biosynthesis
Abstract
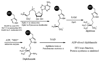
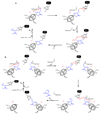
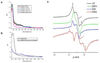
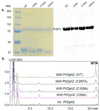
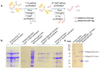
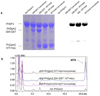
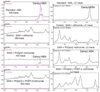
Diphthamide, the target of diphtheria toxin, is a unique posttranslational modification on eukaryotic and archaeal translation elongation factor 2 (EF2). The proposed biosynthesis of diphthamide involves three steps and we have recently found that in Pyrococcus horikoshii (P. horikoshii), the first step uses an S-adenosyl-L-methionine (SAM)-dependent [4Fe-4S] enzyme, PhDph2, to catalyze the formation of a C-C bond. Crystal structure shows that PhDph2 is a homodimer and each monomer contains three conserved cysteine residues that can bind a [4Fe-4S] cluster. In the reduced state, the [4Fe-4S] cluster can provide one electron to reductively cleave the bound SAM molecule. However, different from classical radical SAM family of enzymes, biochemical evidence suggest that a 3-amino-3-carboxypropyl radical is generated in PhDph2. Here we present evidence supporting that the 3-amino-3-carboxypropyl radical does not undergo hydrogen abstraction reaction, which is observed for the deoxyadenosyl radical in classical radical SAM enzymes. Instead, the 3-amino-3-carboxypropyl radical is added to the imidazole ring in the pathway towards the formation of the product. Furthermore, our data suggest that the chemistry requires only one [4Fe-4S] cluster to be present in the PhDph2 dimer.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Diphthamide biosynthesis requires an organic radical generated by an iron-sulphur enzyme.Nature. 2010 Jun 17;465(7300):891-6. doi: 10.1038/nature09138. Nature. 2010. PMID: 20559380 Free PMC article.
-
The asymmetric function of Dph1-Dph2 heterodimer in diphthamide biosynthesis.J Biol Inorg Chem. 2019 Sep;24(6):777-782. doi: 10.1007/s00775-019-01702-0. Epub 2019 Aug 28. J Biol Inorg Chem. 2019. PMID: 31463593 Free PMC article.
-
Dph3 is an electron donor for Dph1-Dph2 in the first step of eukaryotic diphthamide biosynthesis.J Am Chem Soc. 2014 Feb 5;136(5):1754-7. doi: 10.1021/ja4118957. Epub 2014 Jan 22. J Am Chem Soc. 2014. PMID: 24422557 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of Radical Initiation in the Radical S-Adenosyl-l-methionine Superfamily.Acc Chem Res. 2018 Nov 20;51(11):2611-2619. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.8b00356. Epub 2018 Oct 15. Acc Chem Res. 2018. PMID: 30346729 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Auxiliary iron-sulfur cofactors in radical SAM enzymes.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Jun;1853(6):1316-34. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2015.01.002. Epub 2015 Jan 15. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 25597998 Review.
Cited by
-
Genome-wide screening in human embryonic stem cells identifies genes and pathways involved in the p53 pathway.Mol Med. 2025 Mar 13;31(1):97. doi: 10.1186/s10020-025-01141-5. Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 40082762 Free PMC article.
-
YBR246W is required for the third step of diphthamide biosynthesis.J Am Chem Soc. 2012 Jan 18;134(2):773-6. doi: 10.1021/ja208870a. Epub 2011 Dec 21. J Am Chem Soc. 2012. PMID: 22188241 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into diphthamide, key diphtheria toxin effector.Toxins (Basel). 2013 May 3;5(5):958-68. doi: 10.3390/toxins5050958. Toxins (Basel). 2013. PMID: 23645155 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative genomic analysis of the DUF71/COG2102 family predicts roles in diphthamide biosynthesis and B12 salvage.Biol Direct. 2012 Sep 26;7:32. doi: 10.1186/1745-6150-7-32. Biol Direct. 2012. PMID: 23013770 Free PMC article.
-
Open Issues for Protein Function Assignment in Haloferax volcanii and Other Halophilic Archaea.Genes (Basel). 2021 Jun 24;12(7):963. doi: 10.3390/genes12070963. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34202810 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

