Structure-activity relationships on the odor detectability of homologous carboxylic acids by humans
- PMID: 20931179
- PMCID: PMC2964470
- DOI: 10.1007/s00221-010-2430-0
Structure-activity relationships on the odor detectability of homologous carboxylic acids by humans
Abstract
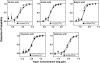
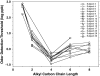
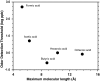
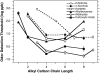
We measured concentration detection functions for the odor detectability of the homologs: formic, acetic, butyric, hexanoic, and octanoic acids. Subjects (14 ≤ n ≤ 18) comprised young (19-37 years), healthy, nonsmoker, and normosmic participants from both genders. Vapors were delivered by air dilution olfactometry, using a three-alternative forced-choice procedure against carbon-filtered air, and an ascending concentration approach. Delivered concentrations were established by gas chromatography (flame ionization detector) in parallel with testing. Group and individual olfactory functions were modeled by a sigmoid (logistic) equation from which two parameters are calculated: C, the odor detection threshold (ODT) and D, the steepness of the function. Thresholds declined with carbon chain length along formic, acetic, and butyric acid where they reached a minimum (ODTs = 514, 5.2, and 0.26 ppb by volume, respectively). Then, they increased for hexanoic (1.0 ppb) and octanoic (0.86 ppb) acid. Odor thresholds and interindividual differences in olfactory acuity among these young, normosmic participants were lower than traditionally thought and reported. No significant effects of gender on odor detectability were observed. The finding of an optimum molecular size for odor potency along homologs confirms a prediction made by a model of ODTs based on a solvation equation. We discuss the mechanistic implications of this model for the process of olfactory detection.
Figures
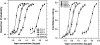

Similar articles
-
Odor detection by humans of lineal aliphatic aldehydes and helional as gauged by dose-response functions.Chem Senses. 2010 May;35(4):289-99. doi: 10.1093/chemse/bjq018. Epub 2010 Feb 26. Chem Senses. 2010. PMID: 20190010 Free PMC article.
-
Olfactory detectability of homologous n-alkylbenzenes as reflected by concentration-detection functions in humans.Neuroscience. 2009 Jun 16;161(1):236-48. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2009.03.029. Epub 2009 Mar 20. Neuroscience. 2009. PMID: 19303922 Free PMC article.
-
Concentration-detection functions for the odor of homologous n-acetate esters.Physiol Behav. 2008 Dec 15;95(5):658-67. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2008.09.021. Epub 2008 Oct 8. Physiol Behav. 2008. PMID: 18950650 Free PMC article.
-
Dose-Response Functions for the Olfactory, Nasal Trigeminal, and Ocular Trigeminal Detectability of Airborne Chemicals by Humans.Chem Senses. 2016 Jan;41(1):3-14. doi: 10.1093/chemse/bjv060. Epub 2015 Oct 17. Chem Senses. 2016. PMID: 26476441 Review.
-
Olfactory perception and blindness: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Psychol Res. 2019 Nov;83(8):1595-1611. doi: 10.1007/s00426-018-1035-2. Epub 2018 Jun 12. Psychol Res. 2019. PMID: 29948185 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
An algorithm for 353 odor detection thresholds in humans.Chem Senses. 2012 Mar;37(3):207-18. doi: 10.1093/chemse/bjr094. Epub 2011 Oct 4. Chem Senses. 2012. PMID: 21976369 Free PMC article.
-
Human Oral Sensitivity to and Taste Modulation by 3-Mercapto-2-Methylpentan-1-ol.Chemosens Percept. 2022;15(2):70-86. doi: 10.1007/s12078-022-09295-w. Epub 2022 Feb 25. Chemosens Percept. 2022. PMID: 35233259 Free PMC article.
-
Richtwerte für Methansäure, Ethansäure und Propansäure in der Innenraumluft : Mitteilung des Ausschusses für Innenraumrichtwerte (AIR).Bundesgesundheitsblatt Gesundheitsforschung Gesundheitsschutz. 2023 Apr;66(4):460-475. doi: 10.1007/s00103-023-03672-w. Bundesgesundheitsblatt Gesundheitsforschung Gesundheitsschutz. 2023. PMID: 36995394 German. No abstract available.
-
Key Odorants from Pig Production Based on Improved Measurements of Odor Threshold Values Combining Olfactometry and Proton-Transfer-Reaction Mass Spectrometry (PTR-MS).Sensors (Basel). 2018 Mar 6;18(3):788. doi: 10.3390/s18030788. Sensors (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29509664 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of the physicochemical properties and key aroma compounds of Beijing roast duck skin sugared by water-in-oil nanoemulsion.Food Chem X. 2025 Jun 14;29:102666. doi: 10.1016/j.fochx.2025.102666. eCollection 2025 Jul. Food Chem X. 2025. PMID: 40606739 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abraham MH, Gola JMR, Cometto-Muñiz JE, Cain WS. The correlation and prediction of VOC thresholds for nasal pungency, eye irritation and odour in humans. Indoor Built Environ. 2001;10:252–257.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

