Molecular networks in drug discovery
- PMID: 20932236
- PMCID: PMC3820486
- DOI: 10.1615/critrevbiomedeng.v38.i2.30
Molecular networks in drug discovery
Abstract
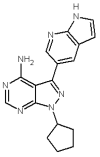
Despite the dramatic increase of global spending on drug discovery and development, the approval rate for new drugs is declining, due chiefly to toxicity and undesirable side effects. Simultaneously, the growth of available biomedical data in the postgenomic era has provided fresh insight into the nature of redundant and compensatory drug-target pathways. This stagnation in drug approval can be overcome by the novel concept of polypharmacology, which is built on the fundamental concept that drugs modulate multiple targets. Polypharmacology can be studied with molecular networks that integrate multidisciplinary concepts including cheminformatics, bioinformatics, and systems biology. In silico techniques such as structure- and ligand-based approaches can be employed to study molecular networks and reduce costs by predicting adverse drug reactions and toxicity in the early stage of drug development. By amalgamating strides in this informatics-driven era, designing polypharmacological drugs with molecular network technology exemplifies the next generation of therapeutics with less of-target properties and toxicity. In this review, we will first describe the challenges in drug discovery, and showcase successes using multitarget drugs toward diseases such as cancer and mood disorders. We will then focus on recent development of in silico polypharmacology predictions. Finally, our technologies in molecular network analysis will be presented.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Polypharmacology: drug discovery for the future.Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2013 Jan;6(1):41-7. doi: 10.1586/ecp.12.74. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23272792 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel computational approaches to polypharmacology as a means to define responses to individual drugs.Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2012;52:361-79. doi: 10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-010611-134630. Epub 2011 Oct 17. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2012. PMID: 22017683 Review.
-
Drugs Polypharmacology by In Silico Methods: New Opportunities in Drug Discovery.Curr Pharm Des. 2016;22(21):3073-81. doi: 10.2174/1381612822666160224142323. Curr Pharm Des. 2016. PMID: 26907944 Review.
-
In silico polypharmacology of natural products.Brief Bioinform. 2018 Nov 27;19(6):1153-1171. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbx045. Brief Bioinform. 2018. PMID: 28460068 Review.
-
Toward structure-multiple activity relationships (SMARts) using computational approaches: A polypharmacological perspective.Drug Discov Today. 2024 Jul;29(7):104046. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2024.104046. Epub 2024 May 27. Drug Discov Today. 2024. PMID: 38810721 Review.
Cited by
-
Repositioned Drugs for Inflammatory Diseases such as Sepsis, Asthma, and Atopic Dermatitis.Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2020 May 1;28(3):222-229. doi: 10.4062/biomolther.2020.001. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2020. PMID: 32133828 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systems Pharmacology Links GPCRs with Retinal Degenerative Disorders.Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2016;56:273-98. doi: 10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-010715-103033. Epub 2015 Mar 23. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2016. PMID: 25839098 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A novel multi-modal drug repurposing approach for identification of potent ACK1 inhibitors.Pac Symp Biocomput. 2013:29-40. Pac Symp Biocomput. 2013. PMID: 23424109 Free PMC article.
-
Consolidation of network and experimental pharmacology to divulge the antidiabetic action of Ficus benghalensis L. bark.3 Biotech. 2021 May;11(5):238. doi: 10.1007/s13205-021-02788-7. Epub 2021 Apr 25. 3 Biotech. 2021. PMID: 33968581 Free PMC article.
-
Cardio-protection of salvianolic acid B through inhibition of apoptosis network.PLoS One. 2011;6(9):e24036. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0024036. Epub 2011 Sep 6. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21915278 Free PMC article.
References
-
- DiMasi JA, Hansen RW, Grabowski HG. The price of innovation: new estimates of drug development costs. J Health Econ. 2003 Mar;22(2):151–85. - PubMed
-
- Martinez B, Goldstein J. Big Pharma Faces Grim Prognosis. Wall Street Journal. 2007
-
- Kola I, Landis J. Can the pharmaceutical industry reduce attrition rates? Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2004 Aug;3(8):711–5. - PubMed
-
- DiMasi JA. The value of improving the productivity of the drug development process: faster times and better decisions. Pharmacoeconomics. 2002;20( Suppl 3):1–10. - PubMed
-
- Janga SC, Tzakos A. Structure and organization of drug-target networks: insights from genomic approaches for drug discovery. Mol Biosyst. 2009 Sep 4; - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

