Pharmacological modulation of diacylglycerol-sensitive TRPC3/6/7 channels
- PMID: 20932261
- PMCID: PMC3267170
- DOI: 10.2174/138920111793937943
Pharmacological modulation of diacylglycerol-sensitive TRPC3/6/7 channels
Abstract
Members of the classic type of transient receptor potential channels (TRPC) represent important molecules involved in hormonal signal transduction. TRPC3/6/7 channels are of particular interest as they are components of phospholipase C driven signalling pathways. Upon receptor-activation, G-protein-mediated stimulation of phospholipase C results in breakdown of phosphatidylinositides leading to increased intracellular diacylglycerol and inositol-trisphosphate levels. Diacylglycerol activates protein kinase C, but more interestingly diacylglycerol directly activates TRPC2/3/6/7 channels. Molecular cloning, expression and characterization of TRP channels enabled reassignment of traditional inhibitors of receptor-dependent calcium entry such as SKF-96365 and 2-APB as blockers of TRPC3/6/7 and several members of non-classic TRP channels. Furthermore, several enzyme inhibitors have also been identified as TRP channel blockers, such as ACA, a phospholipase A(2) inhibitor, and W-7, a calmodulin antagonist. Finally, the naturally occurring secondary plant compound hyperforin has been identified as TRPC6-selective drug, providing an exciting proof of concept that it is possible to generate TRPC-selective channel modulators. The description of Pyr3 as the first TRPC3-selective inhibitor shows that not only nature but also man is able to generate TRP-selective modulators. The review summarizes the data on pharmacological modification of TRPC3/6/7. Sheds lights on the current knowledge and historical development of pharmacological modulators of TRPC3/6/7. Our analysis indicates that Pyr3 and hyperforin provide promising core structures for the development of new, skeletive and more potent modulators of TRPC3/6/7 activity.
Figures

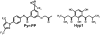
Similar articles
-
Regulation of canonical transient receptor potential (TRPC) channel function by diacylglycerol and protein kinase C.J Biol Chem. 2003 Aug 1;278(31):29031-40. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M302751200. Epub 2003 Apr 29. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12721302
-
Signalling mechanisms for TRPC3 channels.Novartis Found Symp. 2004;258:123-33; discussion 133-9, 155-9, 263-6. Novartis Found Symp. 2004. PMID: 15104179 Review.
-
Complex regulation of the TRPC3, 6 and 7 channel subfamily by diacylglycerol and phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate.Cell Calcium. 2008 May;43(5):506-14. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2007.09.001. Epub 2007 Oct 17. Cell Calcium. 2008. PMID: 17942152 Free PMC article.
-
Differences in TRPC3 and TRPC6 channels assembly in mesenteric vascular smooth muscle cells in essential hypertension.J Physiol. 2017 Mar 1;595(5):1497-1513. doi: 10.1113/JP273327. Epub 2016 Dec 29. J Physiol. 2017. PMID: 27861908 Free PMC article.
-
On the potential role of source and species of diacylglycerol in phospholipase-dependent regulation of TRPC3 channels.Channels (Austin). 2010 May-Jun;4(3):232-40. doi: 10.4161/chan.4.3.12058. Channels (Austin). 2010. PMID: 20458187 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of a non-selective TRPC channel blocker, SKF-96365, on melittin-induced spontaneous persistent nociception and inflammatory pain hypersensitivity.Neurosci Bull. 2012 Apr;28(2):173-81. doi: 10.1007/s12264-012-1213-y. Neurosci Bull. 2012. PMID: 22466128 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulated TRPC5 plays an important role in development of nasal polyps by activating eosinophilic inflammation and NF-κB signaling pathways.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2018 Apr 1;11(4):1935-1945. eCollection 2018. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2018. PMID: 31938299 Free PMC article.
-
Magnesium inhibits Wnt/β-catenin activity and reverses the osteogenic transformation of vascular smooth muscle cells.PLoS One. 2014 Feb 25;9(2):e89525. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0089525. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24586847 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of SKF-96365, a TRPC inhibitor, on melittin-induced inward current and intracellular Ca2+ rise in primary sensory cells.Neurosci Bull. 2011 Jun;27(3):135-42. doi: 10.1007/s12264-011-1018-4. Neurosci Bull. 2011. PMID: 21614096 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelin-1 and endothelin-2 initiate and maintain contractile responses by different mechanisms in rat mesenteric and cerebral arteries.Br J Pharmacol. 2013 Nov;170(6):1199-209. doi: 10.1111/bph.12332. Br J Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23941276 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hofmann T, Obukhov AG, Schaefer M, Harteneck C, Gudermann T, Schultz G. Direct activation of human TRPC6 and TRPC3 channels by diacylglycerol. Nature. 1999;397(6716):259–263. - PubMed
-
- Okada T, Inoue R, Yamazaki K, Maeda A, Kurosaki T, Yamakuni T, Tanaka I, Shimizu S, Ikenaka K, Imoto K, Mori Y. Molecular and functional characterization of a novel mouse transient receptor potential protein homologue TRP7. Ca2+-permeable cation channel that is constitutively activated and enhanced by stimulation of G protein-coupled receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 1999;274(39):27359–27370. - PubMed
-
- Lucas P, Ukhanov K, Leinders-Zufall T, Zufall F. A diacylglycerol-gated cation channel in vomeronasal neuron dendrites is impaired in TRPC2 mutant mice: mechanism of pheromone transduction. Neuron. 2003;40(3):551–561. - PubMed
-
- Chyb S, Raghu P, Hardie RC. Polyunsaturated fatty acids activate the Drosophila light-sensitive channels TRP and TRPL. Nature. 1999;397(6716):255–259. - PubMed
-
- Jörs S, Kazanski V, Foik A, Krautwurst D, Harteneck C. Receptor-induced activation of Drosophila TRP gamma by polyunsaturated fatty acids. J. Biol. Chem. 2006;281(40):29693–29702. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
