Predicting enzyme targets for cancer drugs by profiling human metabolic reactions in NCI-60 cell lines
- PMID: 20932284
- PMCID: PMC2964682
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-11-501
Predicting enzyme targets for cancer drugs by profiling human metabolic reactions in NCI-60 cell lines
Abstract
Background: Drugs can influence the whole metabolic system by targeting enzymes which catalyze metabolic reactions. The existence of interactions between drugs and metabolic reactions suggests a potential way to discover drug targets.
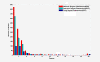
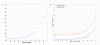
Results: In this paper, we present a computational method to predict new targets for approved anti-cancer drugs by exploring drug-reaction interactions. We construct a Drug-Reaction Network to provide a global view of drug-reaction interactions and drug-pathway interactions. The recent reconstruction of the human metabolic network and development of flux analysis approaches make it possible to predict each metabolic reaction's cell line-specific flux state based on the cell line-specific gene expressions. We first profile each reaction by its flux states in NCI-60 cancer cell lines, and then propose a kernel k-nearest neighbor model to predict related metabolic reactions and enzyme targets for approved cancer drugs. We also integrate the target structure data with reaction flux profiles to predict drug targets and the area under curves can reach 0.92.
Conclusions: The cross validations using the methods with and without metabolic network indicate that the former method is significantly better than the latter. Further experiments show the synergism of reaction flux profiles and target structure for drug target prediction. It also implies the significant contribution of metabolic network to predict drug targets. Finally, we apply our method to predict new reactions and possible enzyme targets for cancer drugs.
Figures





References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

