Symptomatic Bochdalek hernia in an adult
- PMID: 20932385
- PMCID: PMC3043584
- DOI: 10.4293/108680810X12785289144719
Symptomatic Bochdalek hernia in an adult
Abstract
Background and objectives: Bochdalek hernias are congenital diaphragmatic defects resulting from the failure of posterolateral diaphragmatic foramina to fuse in utero. Symptomatic Bochdalek hernias in adults are infrequent and may lead to gastrointestinal dysfunction or severe pulmonary disease. We describe our experience with this rare entity.
Methods: A retrospective chart review was performed on a single patient for data collection purposes.
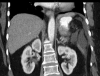
Results: The patient is a morbidly obese 53-year-old female who presented with epigastric pain and diffuse abdominal tenderness. Computed tomography scans of the chest and abdomen revealed a small posterior diaphragmatic defect containing gastric fundal diverticulum. Laboratory work and imaging revealed no other findings. Laparoscopic repair of the Bochdalek hernia was done via an abdominal approach and utilized primary closure with an AlloDerm patch apposed to the defect. The patient has had significant clinical improvement and continues to do well at 9 months postoperatively.
Conclusion: Laparoscopic repair of symptomatic adult Bochdalek hernias can be performed successfully and may result in significant clinical improvement.
Figures
References
-
- Mullins ME, Stein J, Saini SS, Mueller PR. Prevalence of incidental Bochdalek's hernia in a large adult population. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2001;177:363–366 - PubMed
-
- Salacin S, Alper B, Cekin N, Gulmen MK. Bochdalek hernia in adulthood: a review and an autopsy case report. J Forensic Sci. 1994;39:1112–1116 - PubMed
-
- Nitecki S, Mar-Maor JA. Late presentation of Bochdalek hernia: our experience and review of the literature. Isr J Med Sci. 1992;28:711–714 - PubMed
-
- Killeen KL, Mirvis SE, Shanmuganathan K. Helical CT of diaphragmatic rupture caused by blunt trauma. Am J Radiol. 1999;173:1611–1616 - PubMed
-
- Gale ME. Bochdalek hernia: prevalence and CT characteristics. Radiology. 1985;156:449–452 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources