CRL4(Cdt2)-mediated destruction of the histone methyltransferase Set8 prevents premature chromatin compaction in S phase
- PMID: 20932472
- PMCID: PMC2957874
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2010.09.015
CRL4(Cdt2)-mediated destruction of the histone methyltransferase Set8 prevents premature chromatin compaction in S phase
Abstract
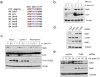
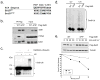
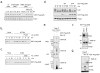
The proper coordination between DNA replication and mitosis during cell-cycle progression is crucial for genomic stability. During G2 and mitosis, Set8 catalyzes monomethylation of histone H4 on lysine 20 (H4K20me1), which promotes chromatin compaction. Set8 levels decline in S phase, but why and how this occurs is unclear. Here, we show that Set8 is targeted for proteolysis in S phase and in response to DNA damage by the E3 ubiquitin ligase, CRL4(Cdt2). Set8 ubiquitylation occurs on chromatin and is coupled to DNA replication via a specific degron in Set8 that binds PCNA. Inactivation of CRL4(Cdt2) leads to Set8 stabilization and aberrant H4K20me1 accumulation in replicating cells. Transient S phase expression of a Set8 mutant lacking the degron promotes premature H4K20me1 accumulation and chromatin compaction, and triggers a checkpoint-mediated G2 arrest. Thus, CRL4(Cdt2)-dependent destruction of Set8 in S phase preserves genome stability by preventing aberrant chromatin compaction during DNA synthesis.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




Comment in
-
SETting the clock for histone H4 monomethylation.Mol Cell. 2010 Nov 12;40(3):345-6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2010.10.033. Mol Cell. 2010. PMID: 21070959 Free PMC article.
-
Cell cycle: Disposing of SETD8.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2010 Dec;11(12):819. doi: 10.1038/nrm3020. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 21102605 No abstract available.
References
-
- Angers S, Li T, Yi X, MacCoss MJ, Moon RT, Zheng N. Molecular architecture and assembly of the DDB1-CUL4A ubiquitin ligase machinery. Nature. 2006;443:590–593. - PubMed
-
- Arias EE, Walter JC. PCNA functions as a molecular platform to trigger Cdt1 destruction and prevent re-replication. Nat Cell Biol. 2006;8:84–90. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

