Interaction of a DNA zip code with the nuclear pore complex promotes H2A.Z incorporation and INO1 transcriptional memory
- PMID: 20932479
- PMCID: PMC2953765
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2010.09.007
Interaction of a DNA zip code with the nuclear pore complex promotes H2A.Z incorporation and INO1 transcriptional memory
Abstract
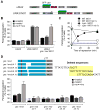
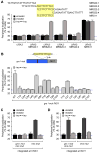
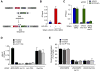
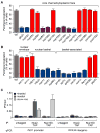
DNA "zip codes" in the promoters of yeast genes confer interaction with the NPC and localization at the nuclear periphery upon activation. Some of these genes exhibit transcriptional memory: after being repressed, they remain at the nuclear periphery for several generations, primed for reactivation. Transcriptional memory requires the histone variant H2A.Z. We find that targeting of active INO1 and recently repressed INO1 to the nuclear periphery is controlled by two distinct and independent mechanisms involving different zip codes and different interactions with the NPC. An 11 base pair memory recruitment sequence (MRS) in the INO1 promoter controls both peripheral targeting and H2A.Z incorporation after repression. In cells lacking either the MRS or the NPC protein Nup100, INO1 transcriptional memory is lost, leading to nucleoplasmic localization after repression and slower reactivation of the gene. Thus, interaction of recently repressed INO1 with the NPC alters its chromatin structure and rate of reactivation.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Akhtar A, Gasser SM. The nuclear envelope and transcriptional control. Nat Rev Genet. 2007;8:507–517. - PubMed
-
- Brickner DG, Light WH, Brickner JH. Quantitative localization of chromosomal loci by immunofluorescence. In: Weissman J, Guthrie C, Fink GR, editors. Methods in Enzymology. Burlington: Academic Press; 2010. pp. 569–580. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

